Figure 4.
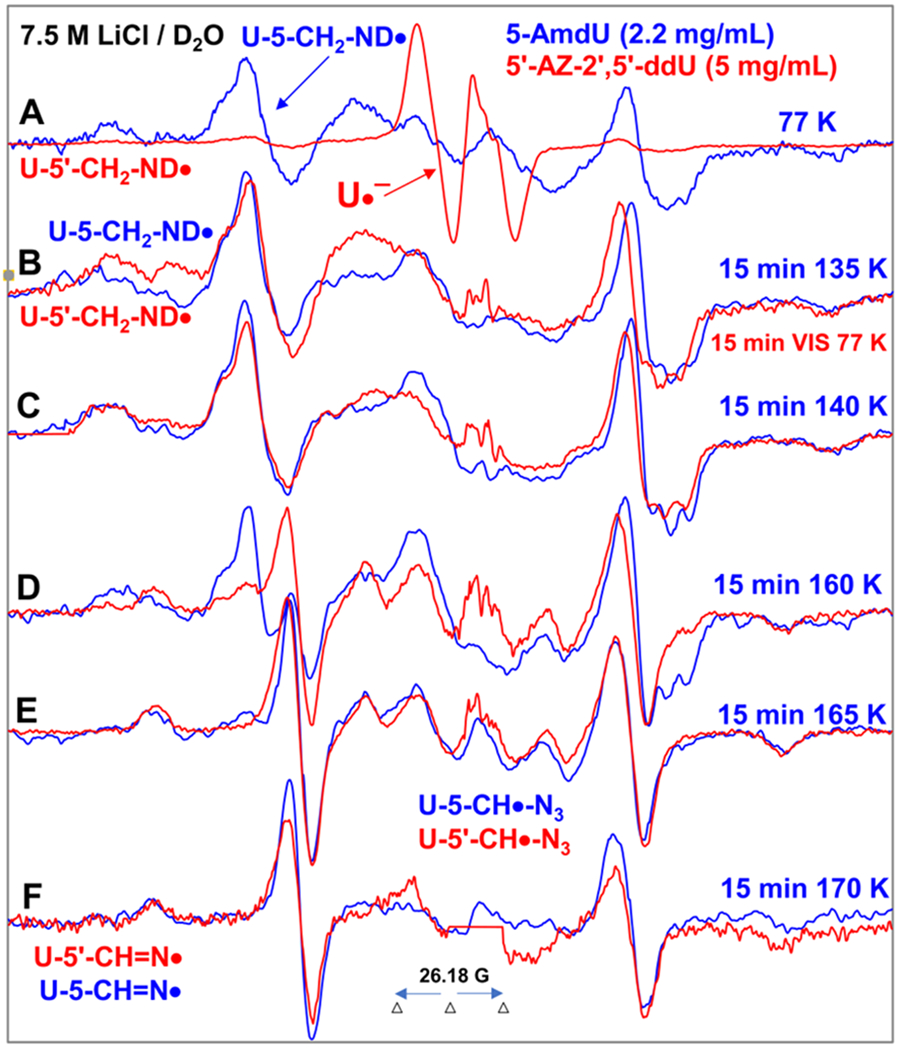
Spectra (A-D) in red were obtained from samples of 5′-AZ-2′,5′-ddU (5) ([5] = 5 mg/mL) after subtraction of the Cl2•− spectrum7–9,49 from the individual experimentally recorded spectrum. (A) EPR spectrum (red) after radiation-produced prehydrated one-electron addition to the same sample of 5 at 77 K in 7.5 M LiCl/D2O. Spectrum (B, red) was obtained after 15 min photoexcitation by a photoflood lamp at 77 K. Spectra (C, red) to (F, red) were obtained via stepwise annealing of the sample for 15 min at 140, 160, 165, and 170 K. All spectra were recorded at 77 K. Sum of two isotropic β-proton couplings is assigned to the central doublet (ca. 90.5 G) found in red spectra (A) to (D); the large central doublet (ca. 82 G) in spectra (D to F, red) is due to one isotropic β-proton coupling. Whereas, the wings in spectra (A) to (F) show the Azz components of the anisotropic nitrogen hyperfine coupling. All spectra were recorded at 77 K. The experimental spectra from AmdU from ref. 7 (2.2 mg/mL, blue) are superimposed in (A) to (F) for comparison.
