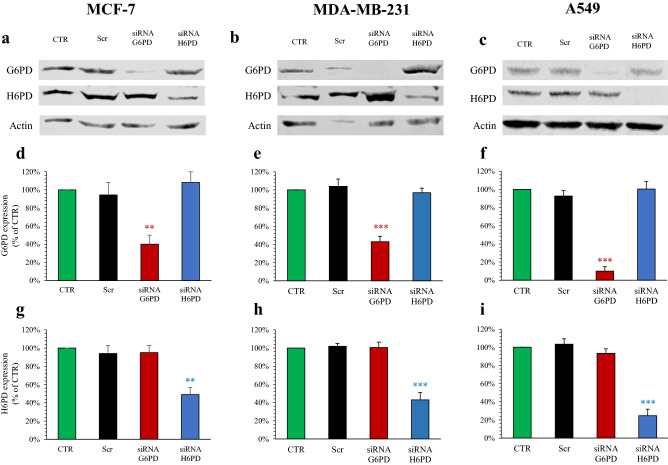
Figure 1.
G6PD and H6PD Gene Expression after siRNA transfection. Representative images of western blot analysis of MCF-7 (a), MDA-MB-231 (b) and A549 (c) (run under the same experimental conditions for each cell line), reporting G6PD, H6PD and Actin expression. Relative densitometry analyses of G6PD and H6PD expression in MCF-7 (d,g), MDA-MB-231 (e,h) and A549 (f,i), under control condition (CTR, green), scramble siRNA (Scr, black), siRNA G6PD (red) and siRNA H6PD (blue). In all cell lines, scramble siRNA-transfected cells did not show significant variations in the levels of G6PD and H6PD with respect to control ones. G6PD siRNA delivery significantly reduced G6PD expression in MCF-7 (d), MDA-MB-231 (e) and A549 (f), while keeping unaltered H6PD expression. Similarly, H6PD siRNA transfection selectively reduced enzyme expression in MCF-7 (g), MDA-MB-231 (h) and A549 (i). Western blot analysis confirmed the efficiency and selectivity of gene silencing in all cancer cell models, documenting the absence of any interference between the trigger enzymes G6PD and H6PD. Data are expressed as % ± SD of respective control condition (n = 3). **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001 vs corresponding scramble. The full-length gels are presented in Supplementary Fig. 1.