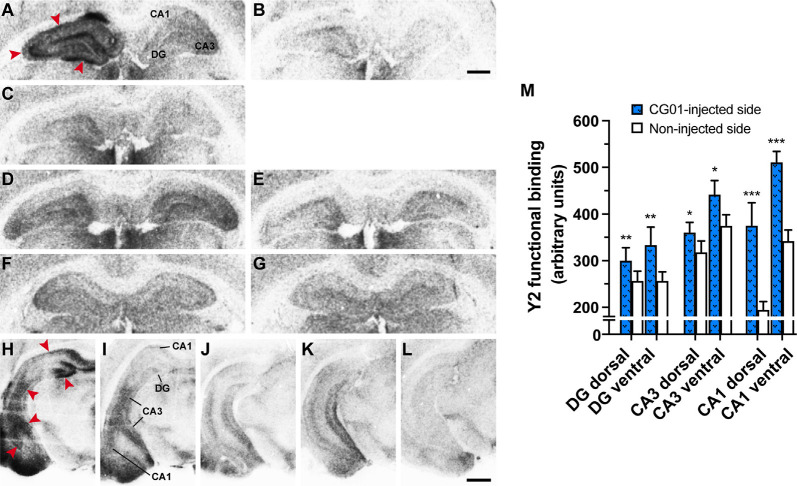
Figure 5.
Unilateral intrahippocampal administration of CG01 increased Y2 transgene expression as seen by increased Y2 functional binding (NPY + Y1 antagonist + Y5 antagonist) in the right dorsal hippocampal DG, CA3, and CA1 of a CG01-injected rat (red arrows) compared to the contralateral non-injected side (A). Basal binding (no addition of NPY; B) and blocking of Y2 binding (NPY + Y1 antagonist + Y5 antagonist + Y2 antagonist; C) are shown in CG01-injected rat. Y2 functional binding is shown in CG07-injected (D) and in naïve rat (F) with corresponding basal binding (E and G, respectively). Increased Y2 functional binding was also seen in DG, CA3, and CA1 in ventral part of the CG01-injected hippocampus (red arrows; H) compared to non-injected hippocampus (I). Y2 functional binding displayed in ventral hippocampus of CG07-injected rat (J) and in naïve rat (K) while (L) shows basal binding in CG01-injected ventral hippocampus. Magnification bars = 1 mm in panels (A–G) and 1.5 mm in panels (H–L). Densitometric measurements confirmed that CG01 increased Y2 functional binding in dorsal and ventral parts of hippocampus after unilateral intrahippocampal administration compared to the contralateral non-injected side (M). *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001 vs. non-injected side, Kruskal–Wallis ANOVA followed by Wilcoxon matched-pairs signed rank tests. Data are means ± SEM (n = 10–12).