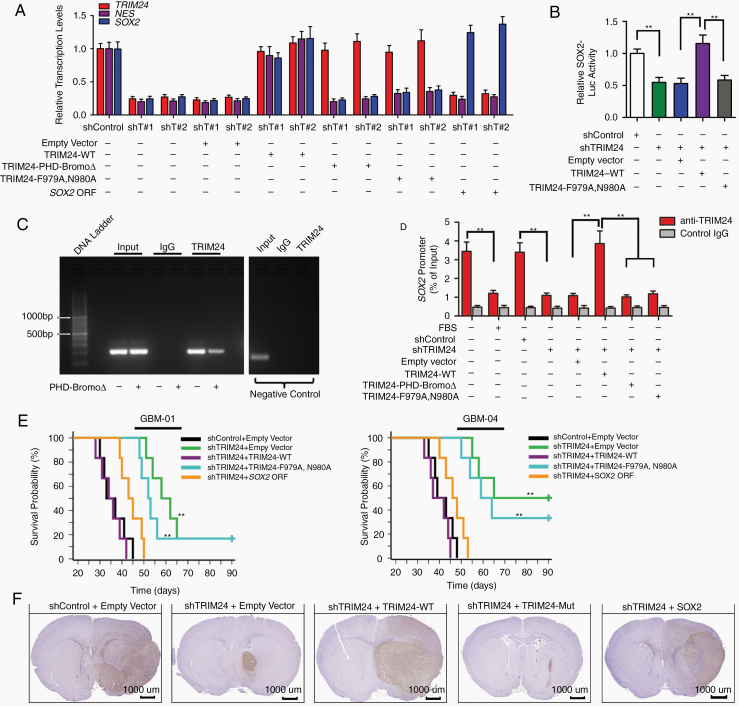
Fig. 3.
TRIM24 impacts GBM stemness via driving Sox2 expression. (A) Real-time reverse transcription (RT) PCR analyses of gene expression profiles in GSCs. Shown are relative levels of TRIM24, Nestin (encoded by NES), and Sox2 in GSCs derived from GBM-01 cells. (B) Dual luminescence assay was employed to measure the relative activity of Sox2 promoter after lentiviral infection. Shown are the data of GSCs derived from GBM-01 cells. **P < 0.01. (C) ChIP analysis of the Sox2 promoter using standard PCR in GSCs derived from GBM-01 cells. Shown are gel electrophoresis images using primers corresponding to the site that presents the most binding affinity (-544 to -362 fragment in the Sox2 promoter). The results of negative control KIAA0066 are also presented. (D) Real-time PCR analyses of the ChIPed DNA using primers to amplify the fragment encompassing the -544 to -362 site of Sox2 promoter in GSCs derived from GBM-01 cells. **P < 0.01. (E) Kaplan–Meier method was employed to demonstrate the survival curves of orthotopic transplanted nude mice (1000 GSCs per animal, n = 6 per group). The log-rank test was used to determine statistical significance. P < 0.01 between shTRIM24 + empty vector and shTRIM24 + TRIM24-WT group; P < 0.01 between shTRIM24 + TRIM24-WT and shTRIM24 + TRIM24-F979A,N980A group; P < 0.01 between shTRIM24 + empty vector and shTRIM24 + Sox2 ORF group. **P < 0.01. (F) Differently treated GSCs derived from GBM-01 cells were transplanted into nude mice (1000 cells per animal, n = 5 per group) and all the mice were sacrificed when development of neurologic signs was observed in any group. Representative immunohistochemical images of orthotopic xenografts are shown. Scale bars represent 1 mm. Expanded view of images is presented in Supplementary Figure 9.