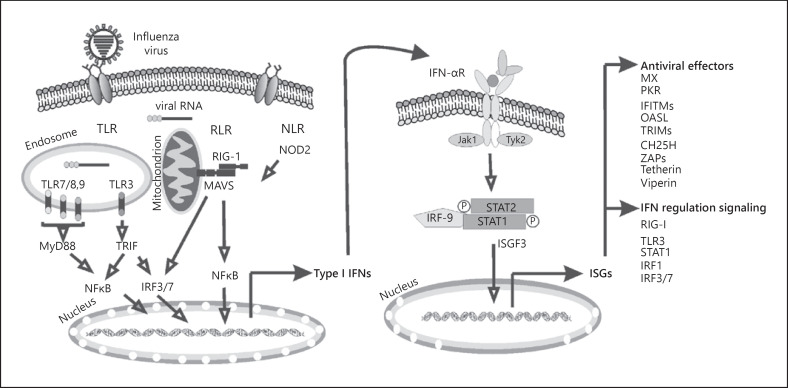
Fig. 1.
Induction of type I IFNs and ISGs by influenza virus. Innate immune cells, such as macrophages and lung epithelial cells, produce type I IFNs after sensing IAV genomic RNA using various PRRs. In infected and neighboring cells, type I IFN signaling activates the JAK-STAT pathway, leading to transcription of ISGs, the products of which initiate intracellular antiviral effectors that limit the spread of the viruses. IFN, interferon; ISG, IFN-stimulated gene; PRR, pattern recognition receptor; JAK, Janus kinase; STAT, signal transducer and activator of transcription; TLR, Toll-like receptor; RLR, RIG-I like helicase; NLR, nucleotide-binding domain and leucine-rich-repeat-containing protein.