Figure 2.
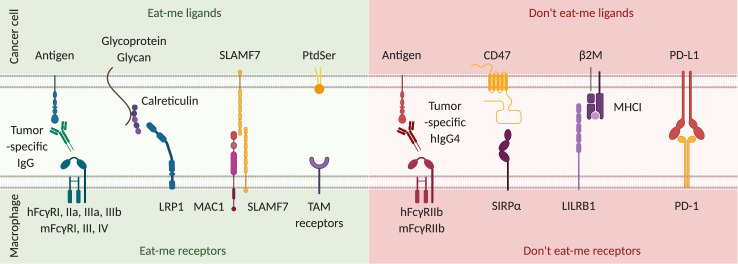
Signals modulating phagocytosis initiation. From left to right: tumor-specific IgG antibodies opsonize cancer cells by binding to tumor antigens. Fcγ receptors (FcγR) expressed on macrophages recognize the constant region of these antibodies and initiate antibody-dependent cell phagocytosis.103 In humans, the intracellular portion of FcγRI, IIa, IIIa and IIIb possess an immunoreceptor tyrosine-based activation motif (ITAM) that leads to pro-phagocytic activity. In mice, FcγRI, III and IV possess an ITAM. Calreticulin translocation to the surface is induced by cellular stress and DNA damage.104 Once on the surface of cancer cells, it is stabilized by glycoproteins and glycans and binds to the lipoprotein receptor-related protein 1 (LRP1) on phagocytes. The exact mechanism of action of signaling lymphocytic activation molecule family member 7 (SLAMF7) is unclear, but it promotes cytoskeletal reorganization required for phagocytosis105 through interaction with macrophage antigen 1 (MAC1) on phagocytes. Phosphatidylserine (PtdSer) is specifically expressed by apoptotic cells and binds to many different receptors among which those of the tumor-associated macrophage (TAM) family (TYRO3, AXL, MerTK) are the best described. It induces efferocytosis, which is a phagocytic process specific for the uptake of apoptotic cells. Eat-me receptor activity is counterbalanced by don’t eat me receptors. First, in both humans and mice, FcγRIIb possesses an immunoreceptor tyrosine-based inhibition motif (ITIM) that negatively regulates initiation of phagocytosis. In humans, IgG4 binds with the highest affinity to FcγRIIb. However, as IgG4 has much greater affinity to the pro-phagocytic FcγRI, the exact role for FcγRIIb expression in vivo is still unknown. In mice, IgG1, IgG2a and IgG2b all bind with low affinity to FcγRIIb.103 CD47 is the most important “don’t eat me” ligand. SIRPα, its receptor on macrophages, inhibits myosin II polymerization, which is a critical step in initiation of cell engulfment. Major histocompatibility complex class I (MHC I) expression by cancer cells also confers protection against phagocytosis. Leukocyte immunoglobulin-like receptor 1 (LILRB1) binding to the β2-microglobulin component of MHC I prevents phagocytosis.106 Finally, programmed cell death protein 1 (PD-1) expression on macrophages is correlated with a lower phagocytic activity, which is restored in PD-1 deficient macrophages. Thus, PD-1 activation by its ligand PD-L1 expressed by cancer cells is another inhibitory signal for phagocytosis.35 Overall, the balance of signaling through eat-me and don’t eat-me receptors will determine initiation of the phagocytic process.