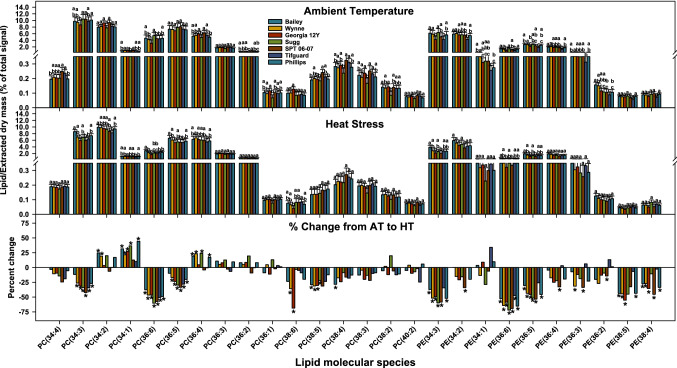
Figure 4.
Changes in the amount of phosphatidylcholine (PC) and phosphatidylethanolamine (PE) molecular species, as percentage of total mass spectral signal, in peanut anthers in response to heat stress. Lipid species shown were those that passed both the limit of detection (LOD > 0.0005 nmol) and coefficient of variation (CoV < 0.3) cutoffs (see “Materials and methods” for more details). Values shown are least-squares means. Error bars represent standard errors about the least-squares mean of 16 observations (2 years × 2 blocks × 4 replications) except for Sugg and SPT 06-07, which have 8 observations (1 year × 2 blocks × 4 replications). Least-squares means with different letters are significantly different according to Fisher’s least significant difference (LSD) test at α = 0.05. An asterisk (*) above bars indicate a significant difference at α = 0.05 between AT and HT for that genotype. AT, ambient temperature (31/22 °C for 2018 and 28/22 °C for 2019; average day/night temperatures during the 17-days and 18-days treatment periods in 2018 and 2019, respectively); HT, high temperature (41/27 °C for 2018 and 38/26 °C for 2019). Lipid molecular species are identified as total acyl carbons: total double bonds. Breaks on the y axis indicate a change in scale. Data from 2 years (2018 and 2019) were pooled together for analysis.