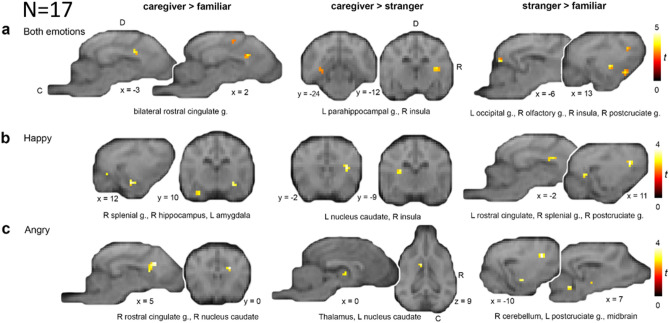
Figure 1.
Visual presentation of caregiver (compared to the familiar person or stranger; independent of emotional facial expression) elicited activation increases in areas associated with the attachment system in humans, whereas visual presentation of the stranger (compared to the familiar person) mainly recruited motor and visual processing regions. The caregiver revealed activation in caudate regions for both happy and angry emotional facial expressions. Results are displayed at p < 0.005 with a minimum cluster size of 5 voxels (see Table 2 for details), projected onto the mean structural image derived from all dogs. Coordinates refer to the canine breed-averaged atlas65. The first sagittal and coronal planes (a, first row) and transverse plane (c, last row) show the anatomical locations caudal (C), dorsal (D), and right hemisphere (R); all sagittal and coronal planes displayed have the same orientation. Group-based comparison of caregiver against familiar person (caregiver > familiar person), caregiver against stranger (caregiver > stranger) and stranger against familiar person (stranger > familiar person) are displayed (a) regardless of emotional facial expression, (b) for happy emotional facial expressions, and (c) for angry emotional facial expressions. D dorsal, C caudal, g. gyrus, R right, t t-value.