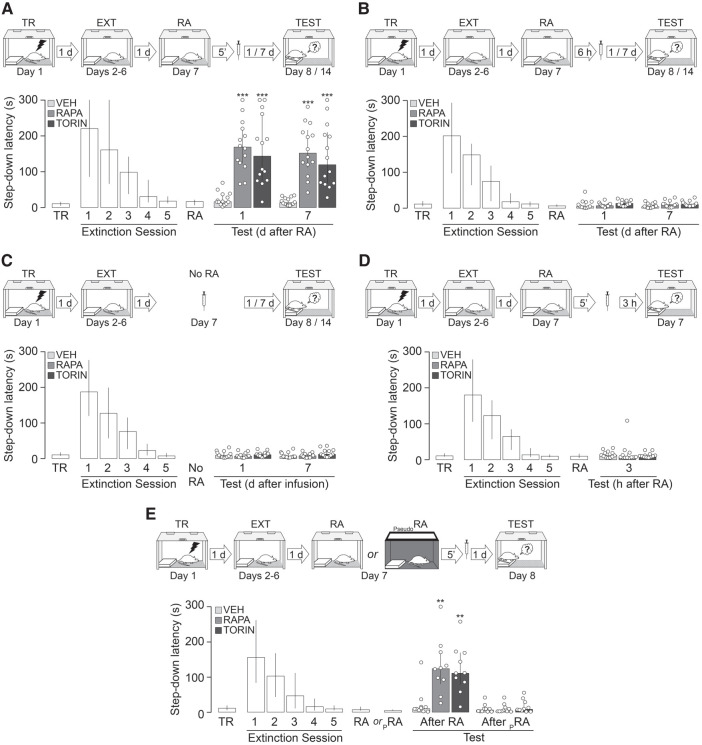
Figure 1.
mTOR is required for fear-motivated avoidance extinction memory reconsolidation. (A) Animals were trained in SDIA (TR; 0.4 mA/2 sec) and beginning 24 h later submitted to one daily extinction session for five consecutive days (EXT). Twenty-four hours after the last session, extinction memory was reactivated (RA) and, 5 min thereafter, the animals received bilateral intradorsal CA1 infusions of vehicle (VEH; 5% DMSO in saline), rapamycin (RAPA; 0.02 µg/side) or TORIN (0.20 µg/side). Retention was assessed 1 and 7 d later (Test). (B) Animals were treated as in A except that they received intra-CA1 infusions of VEH, RAPA, or TORIN 6 h after RA. (C) Animals were treated as in A, except that they received VEH, RAPA, or TORIN in dorsal CA1 24 h after the last extinction session in the absence of RA (No RA). (D) Animals were treated as described in A, except that VEH, RAPA, or TORIN were given 5 min after RA and retention was assessed 3 h later. (E) Animals were treated as in A, except that a subgroup of animals received VEH, RAPA, or TORIN 5 min after an extinction pseudoreactivation session in an avoidance training box rendered nonaversive for SDIA-trained animals. The nonaversive box was similar in dimensions to the SDIA training box, but it was made of dark gray wood and had a Plexiglas platform. (PRA) Pseudoreactivation session. Data are expressed as median ± IQR. (**) P < 0.01, (***) P < 0.001 versus VEH in Dunn's multiple comparisons after Kruskal–Wallis test.