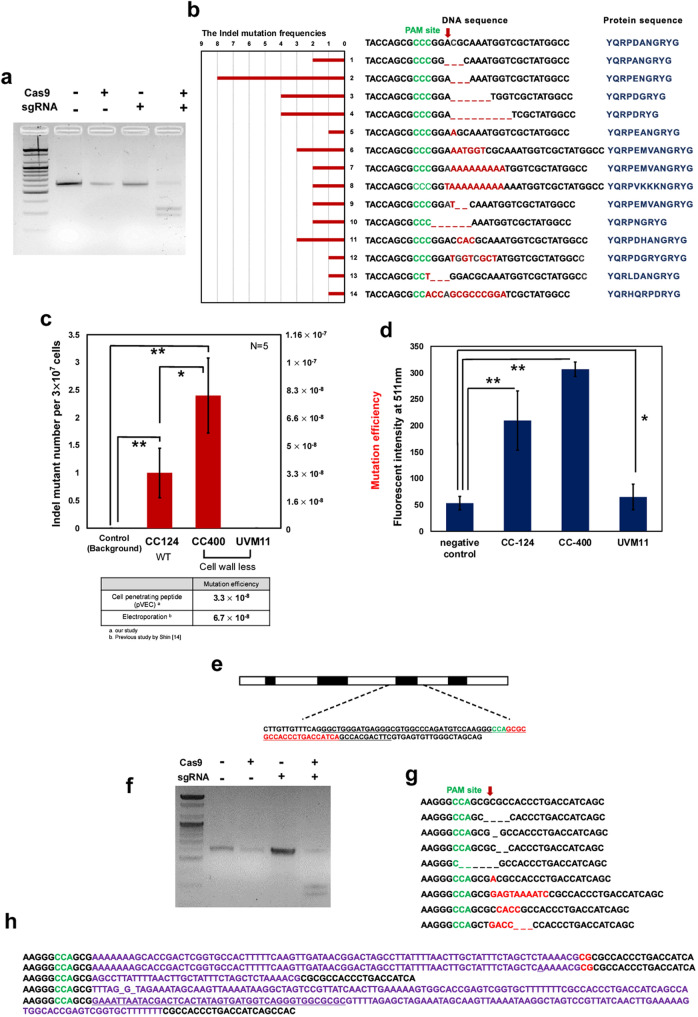
Figure 3.
Gene disruption of Maa7 responsible for tryptophan synthase beta unit (TSB) and gene disruption of FKB12. (a) In-vitro cleavage assay. PCR amplicon having a size of ~ 600 bp was cleaved into two fragments having size of 350 bp and 250 bp. Template DNA of 100 ng was used for the assay and 600 ng of Cas9 and 500 ng of sgRNA were used for in-vitro cleavage assay. Detailed methodology was described in the method part. (b) The Indel mutation cases for in-vivo genome editing experiments. The PAM site is shown in green, and the cleavage point by sgRNA is shown as a red arrow. (c) Indel mutation efficiency of C. reinhardtii subspecies CC124, cell wall-less mutant CC400 and UVM11. For cell wall-less mutant, a starch-embedding method was used for spreading. (d) Protein(FITC-BSA) delivery into C. reinhardtii subspecies by 8 μM of pVEC. Fluorescent intensity of FITC at 511 nm was measured. The washed sample was resuspended in 200ul of TAP media and its fluorescent intensity at 511 nm was measured by a spectrofluorophotometer with excitation wavelength of 475 nm. (e) Description of FKB 12 locus. Underlined sequences refer to CDS, green-sequence refer PAM site, and red-sequence refer sgRNA target site. (f) In-vitro cleavage assay using PCR amplicon of 600 bp. (g) Indel mutation cases for in-vivo genome editing experiments. (h) Insertion of in-vitro transcription DNA template. The data represent the average of n = 5 replicate experiments. Standard deviation bars are shown. **Significantly different (Student’s t-test, p < 0.05) and *Significantly not different (Student’s t-test, p > 0.05).