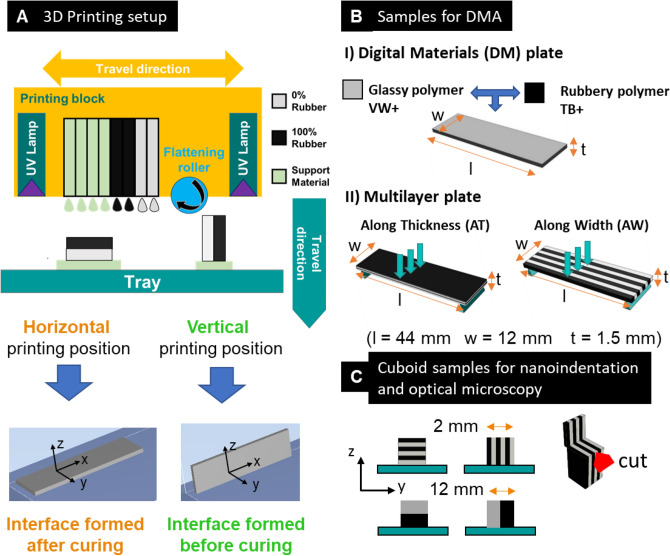
Figure 1.
(A) Scheme of the polyjet printing process considering bimaterial samples fabricated in horizontal or vertical printing position. The two different printing modalities imply that the bimaterial interface is formed after or before UV curing. (B) Plate-like samples consisting of I) digital materials and II) multilayer composites alternating compliant (TangoBlackPlus, TB +) and stiff (VeroWhitePlus, VW +) layers stacked either along the thickness (AT) or the width (AW) of the plate. All samples were assessed with Dynamic Mechanical Analysis (DMA). C) 3D-printed bimaterial cuboid specimens used to characterize interface size with nanoindentation (top) and optical microscopy (bottom). Before nanoindentation, sample surface was smoothed with cryomicrotome: the red arrow indicates the direction of the cut, perpendicular to the interface.