Fig. 2 |. AKBA is wedged between the two domains of Stable-5-LOX.
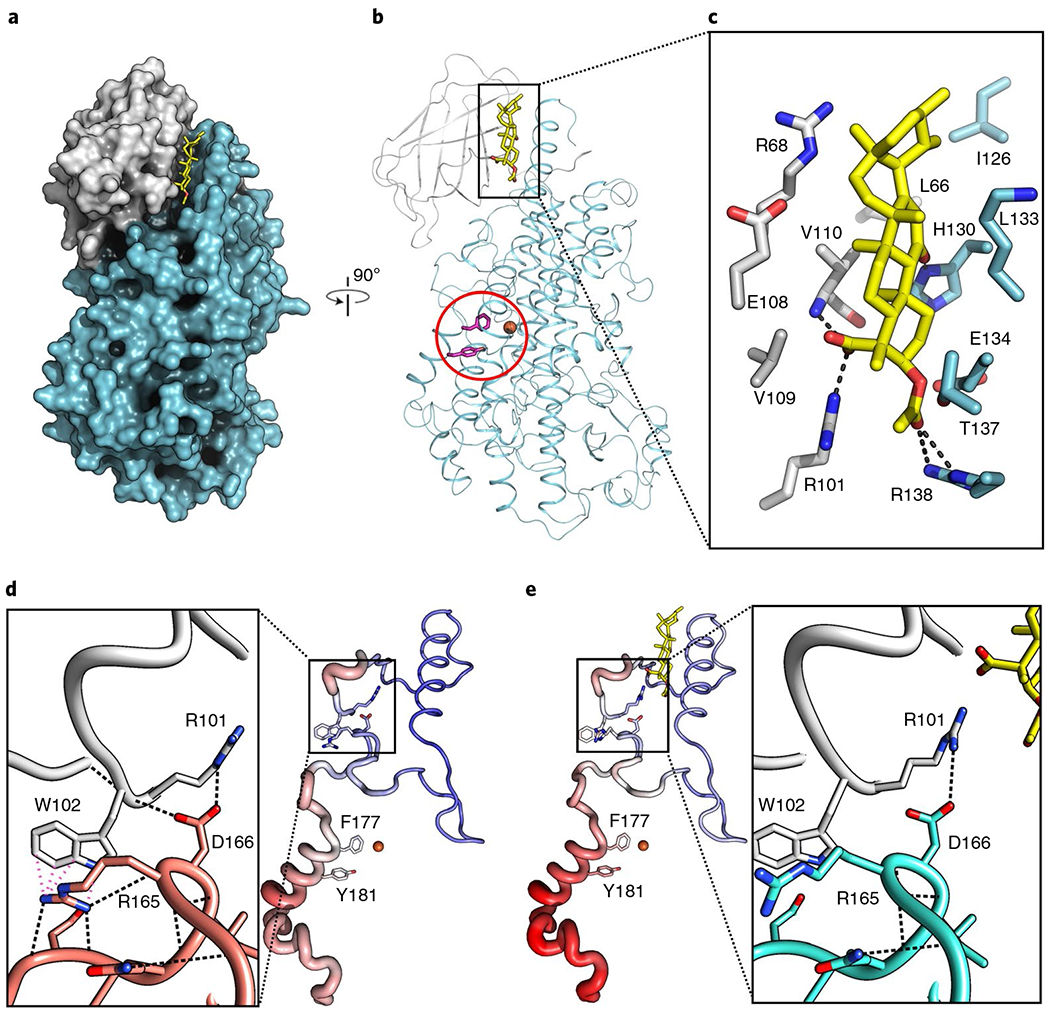
a, A surface rendering of Stable-5-LOX, with the amino-terminal domain in gray and catalytic domain in cyan. AKBA (stick rendering, C, yellow; O, red) lies in a crevice between the two domains. b, The corresponding ribbon diagram, rotated 90°, with the catalytic Fe as an orange sphere and the amino acids that close off the active site in stick rendering (magenta, Phe177, Tyr181). c, Stick rendering of amino acids that form the AKBA-binding site. d,e, Detail of the domain interface in Stable-5-LOX (3O8Y) (d) and the AKBA-bound structure (e). H-bond and cation–π interactions according to Chimera50 are shown as black and pink dashed lines, respectively. The loss of these interactions may contribute to increased B factors in helix-α2, which covers the 5-LOX active site. Tube renderings are of amino acids 100–210 in the apo-(d) and AKBA-occupied structures (e). Tube diameter increases with increasing B factor, accompanied by coloring changes from blue (cool) to red (hot).
