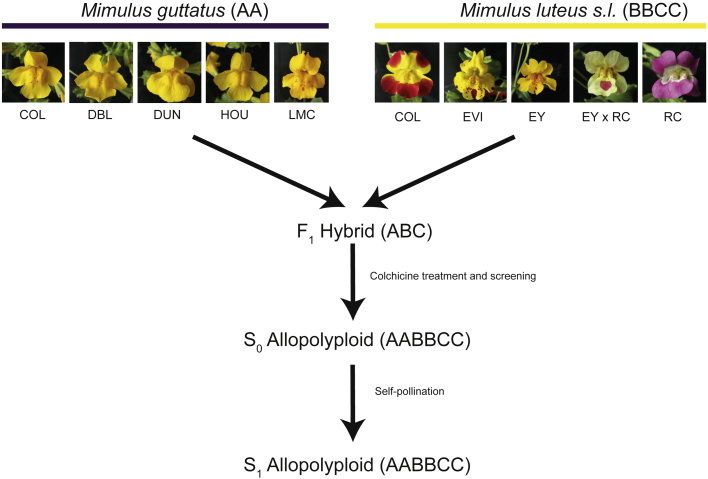
Figure 1.
Diagram of the Experimental Design Used to Generate Synthetic Hybrid (Triploid, ABC) and Allohexaploid (AABBCC) Monkeyflowers (Mimulus spp.).
Five populations were used for each of the parental species, diploid M. guttatus (AA) and the ancient allotetraploid M. luteus sensu lato (BBCC). For M. guttatus, we included three introduced populations in the British Isles (COL, DBL, and HOU) and two native populations (DUN and LMC). For M. luteus s.l. we included two introduced populations from the British Isles (COL and EVI), two native populations of two varieties (M. luteus var. luteus [EY] and M. luteus var. variegatus [RC]), and an experimental hybrid between the two varieties (EY × RC). F1 seeds were treated with colchicine and screened using flow cytometry to identify experimental polyploids, which were then brought to flower and self-fertilized to generate S1 seeds. F1 and S1 seeds were used in all subsequent experiments. Population details are given in Supplemental Table 2.