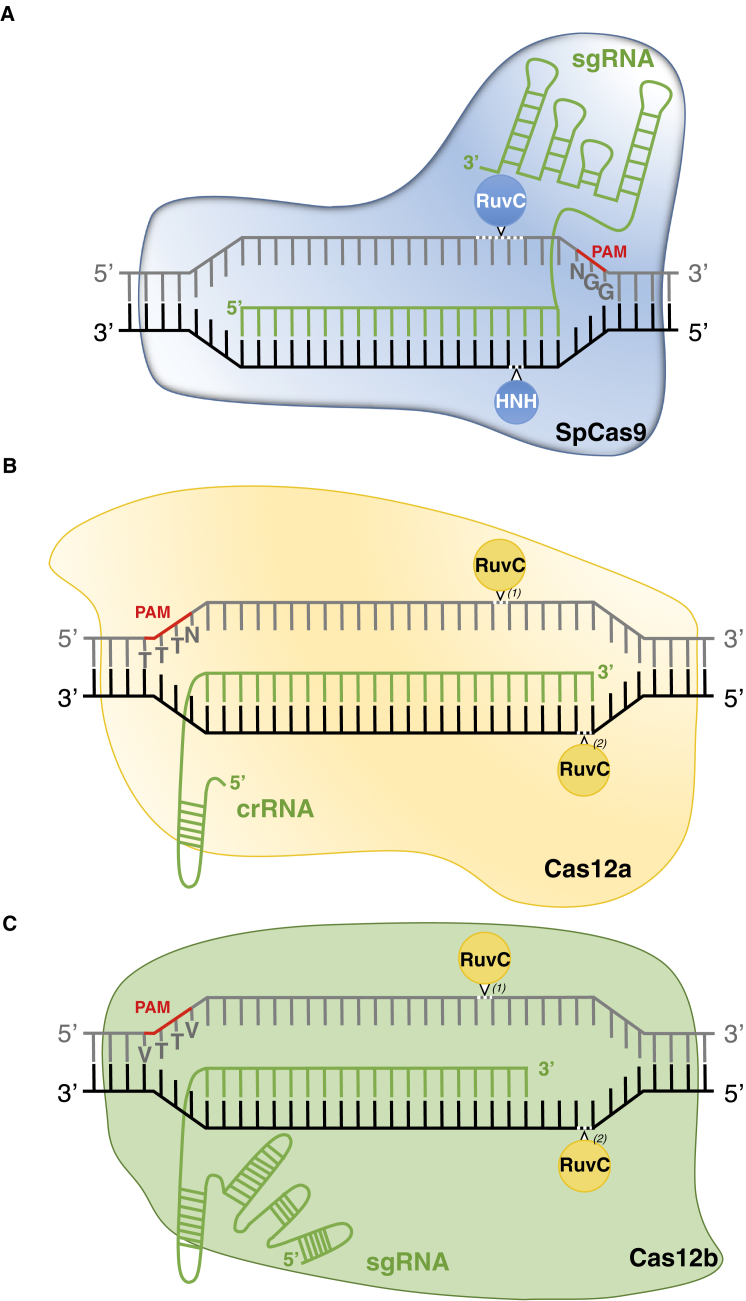
Figure 1.
CRISPR-Cas Systems Used for Genome Editing in Plants.
(A) The CRISPR-SpCas9 system comprised of the endonuclease SpCas9, harboring RuvC and HNH catalytic domains, and the sgRNA that guides the complex to an endogenous target sequence upstream of a G-rich PAM (5′-NGG-3′), leading to blunt and/or staggered DNA breaks.
(B) The CRISPR-Cas12a system involves the endonuclease Cas12a that is guided to the target locus, downstream of a T-rich PAM (5′-TTTN-3′), by a short crRNA, leading to a staggered DNA cleavage by a single RuvC domain after conformational changes: (1) and (2).
(C) The CRISPR-Cas12b system relies on a Cas12b endonuclease, harboring a single RuvC catalytic domain that mediates staggered DNA cleavage—(1) and (2)—and an sgRNA that targets the complex to a specific site downstream of a T-rich PAM (5′-VTTV-3′). The schemes are not at scale and are for illustrative purposes only.