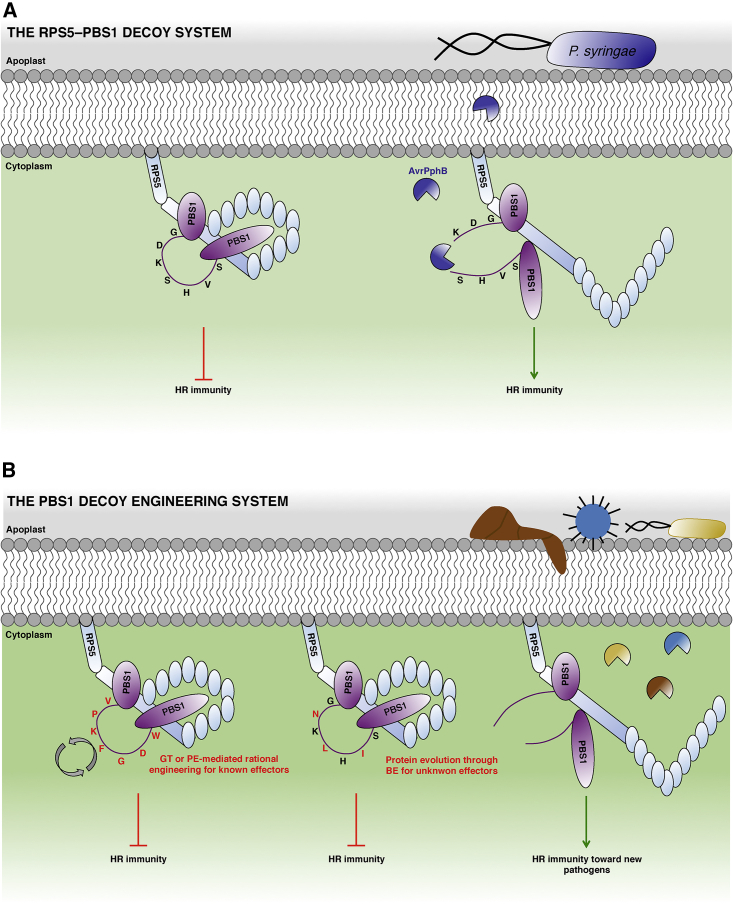
Figure 6.
Representative Model of the Natural and Engineered RPS5-PBS1 Decoy Systems.
(A) RPS5 and PBS1 form an inactive preactivation complex at the plasma membrane. Upon cleavage of the GDKSHVS motif in the activation loop of PBS1 by the Pseudomonas syringae AvrPphB type III protease, RPS5 senses the conformational change of PBS1, leading to the activation of RPS5-mediated HR.
(B) Using CRISPR precision editing tools, it is possible to replace the AvrPphB target cleavage sequence of PBS1 by a motif recognized by another secreted protease, such as the AvrRpt2 effector that cleaves the VPKFGDW sequence. GT or prime editing (PE) tools can be used to replace the initial target cleavage sequence to confer immunity toward pathogens (fungi, bacteria, and viruses) that secrete proteases with known cleavage recognition motifs. Alternatively, protein evolution using base editing (BE) can generate punctual amino acid shifts to generate potential new cleavage sequences. The functionality of these PBS1 variants can be screened toward pathogens that secrete proteases with unknown molecular characteristics, potentially conferring new sources of crop resistance.
The schemes are not at scale and are for illustrative purposes only.