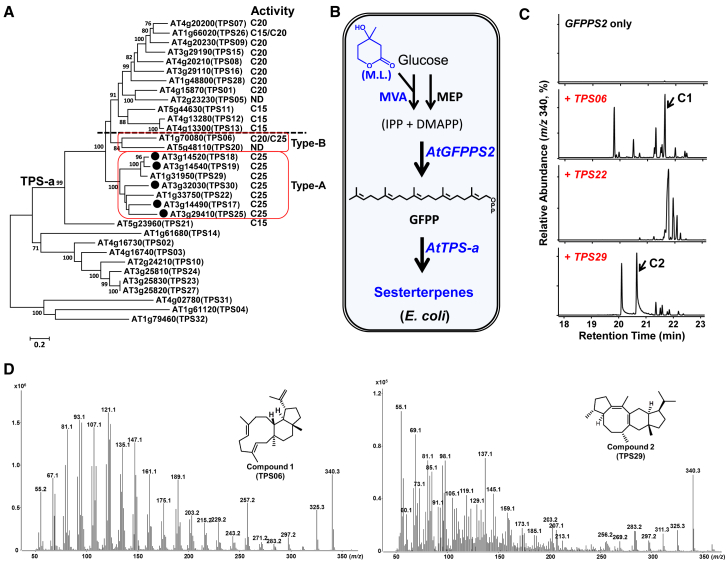
Figure 1.
Sesterterpene Synthases in Arabidopsis and Structures of the Main Products of TPS06 and TPS29.
(A) Phylogenetic analyses of 32 TPS proteins from A. thaliana (Columbia-0 ecotype) using the maximum-likelihood method. Bootstrap values (based on 1000 replicates) >75% are shown for the corresponding nodes. The five known Arabidopsis sester-TPSs are marked with black dots, and the functionally identified sester-TPSs are boxed in red (type A and type B). ND, not determined.
(B) Scheme for screening sester-TPS genes using the E. coli system. MEP, 2-C-methyl-D-erythritol 4-phosphate pathway; ML, mevalonolactone; MVA, mevalonate pathway.
(C) GC–MS analysis (SIM mode, m/z 340 for C25H40) of the sesterterpenes produced in E. coli harboring different TPS-a genes from Arabidopsis: upper panel, AtTPS06; middle panel, AtTPS22; bottom panel, AtTPS29. AtTPS06, a multi-product enzyme, produces more than ten different sesterterpenes from GFPP.
(D) Mass spectra and chemical structures of the main sesterterpene products of TPS06 (C1, left) and TPS29 (C2, right).