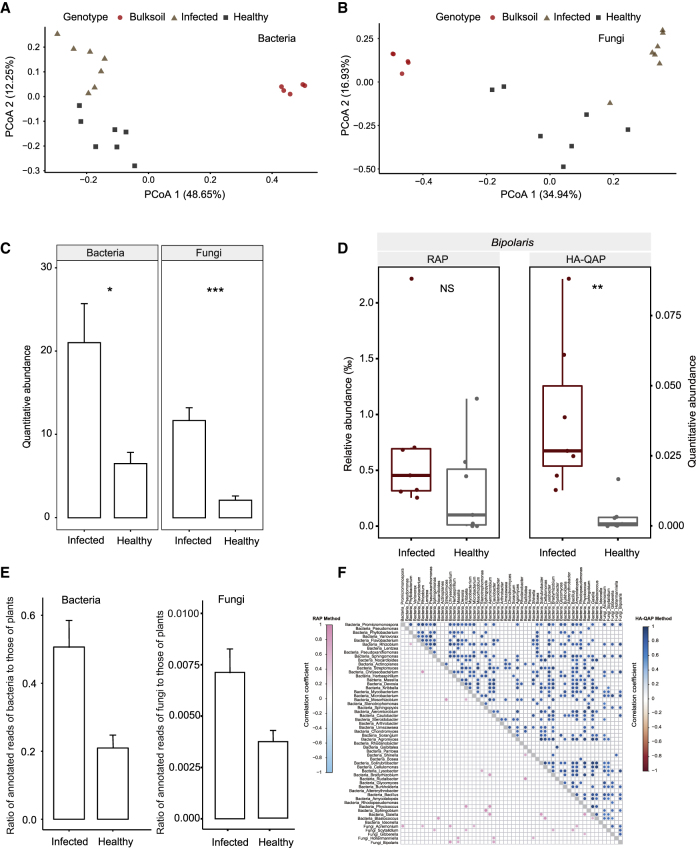
Figure 6.
HA-QAP Reveals Microbial Load Increase in Wheat Plant with Root Rot Disease.
(A and B) Principal coordinates analysis of Bray–Curtis distances showing that infected and healthy roots formed distinct clusters in the bacterial (A) or fungal (B) microbiome. Each point corresponds to a sample: infected root samples, triangles; healthy root samples, squares; bulk soil samples, circles.
(C) Infected root samples had significantly higher bacterial and fungal load than healthy roots. Quantitative abundance represents the copy-number ratio of bacterial 16S rRNA genes and fungal ITS relative to plant genome.
(D) Relative versus quantitative abundance of the potential disease-associated pathogenic genus Bipolaris in healthy and infected samples with root rot disease assessed by RAP and HA-QAP. Quantitative abundance represents the copy-number ratio of fungal ITS relative to plant genome.
(E) Metagenomic data showing higher ratios of bacterial (left) and fungal (right) reads to host plant reads in infected root samples (infected samples, n = 4; healthy samples, n = 4).
(F) Genus co-occurrence patterns within the top 55 most abundant genera and the potential disease-associated pathogenic genus Bipolaris detected by RAP and HA-QAP. Pairwise correlations between taxon abundances were calculated using RAP (lower triangle) and HA-QAP (upper triangle). Significant correlations (two-sided adjusted test, false discovery rate < 0.05) are represented by circles; the color of each circle represents the correlation coefficient (Spearman's ρ). The taxa are firstly ranked according to the bacterial and fungal domain and then ordered by the individual's quantitative abundance within the same domain. The leftmost/top represents the most highly abundant.
For all analyses (except E), the number of biological replicates is as follows: infected root samples, n = 7; healthy root samples, n = 7; bulk soil samples, n = 5. Error bars represent SD calculated from replicates. Statistical significance was determined by Wilcoxon rank-sum test. Asterisks indicate statistically significant differences (*P < 0.05; **P < 0.01). NS, not significant.