FIGURE 2.
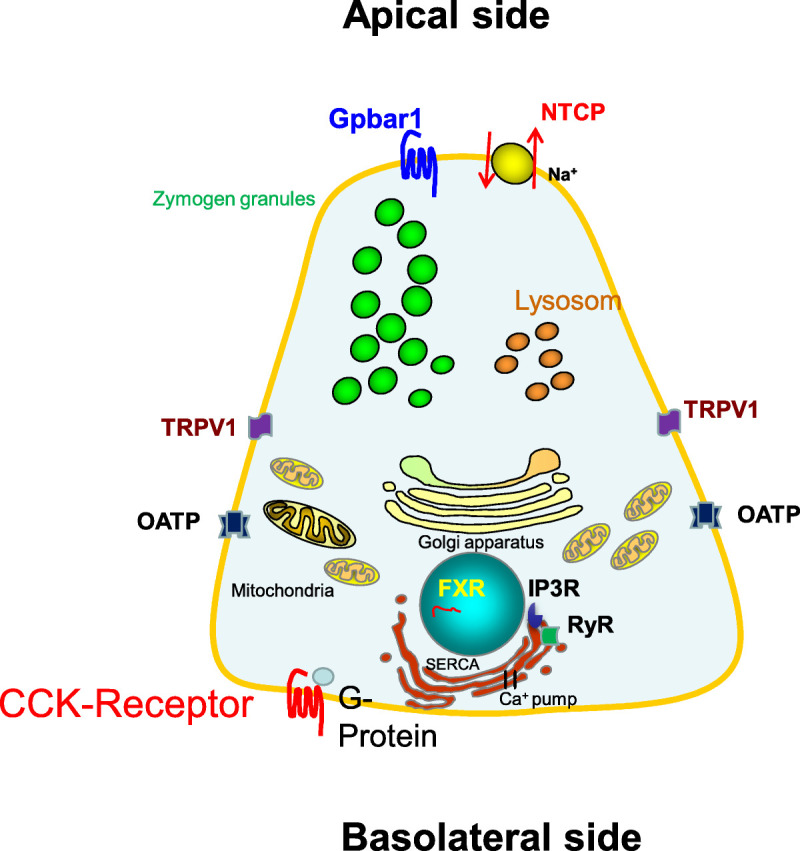
Acinar cell and the relevant BAs transporters and receptors involved in AP. Bile acids can enter the acinar cell via receptors on the membrane such as Gpbar1 and a variety of transporters. They then intracellularly act via FXR in the nuclear, and RyR and IP3Rs at the ER. Bile acids can induce a sustained Ca2+ release from the ER and apical vesicles into the cytosol.
