Figure 2.
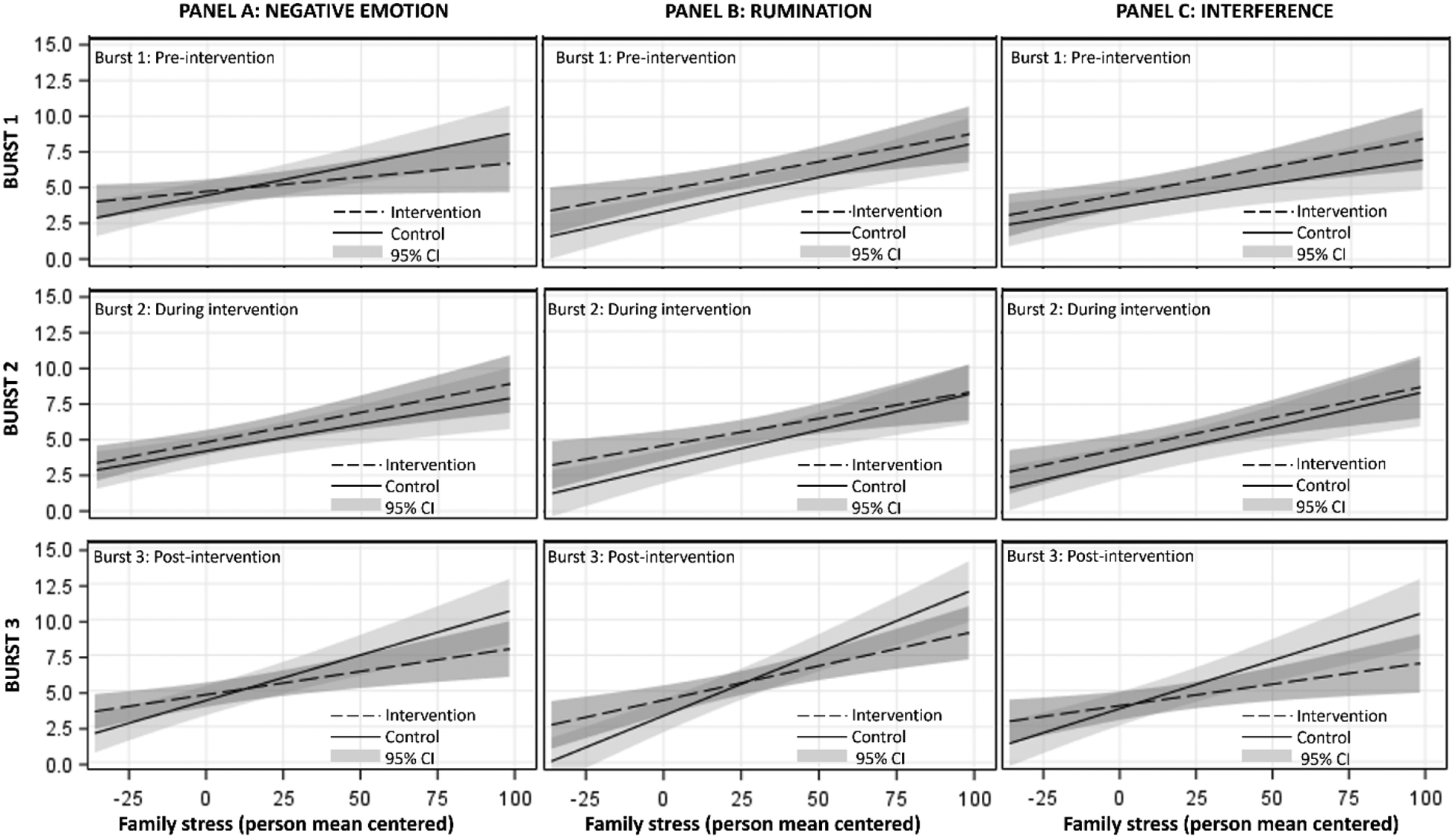
Moment-level associations between family stress and negative emotion, rumination and interference, by burst for the average participant in the intervention and control conditions
Panel A displays associations between family stress and negative emotion at Bursts 1, 2 and 3. Panel B displays associations between family stress and rumination at Bursts 1, 2 and 3. Panel C displays associations between family stress and interference at Bursts 1, 2 and 3. Note: Negative emotion, rumination and interference were square root transformed to reduce the positive skew. Covariates included mean levels of family stress (grand mean centered), weekend status (0=weekday), day in the study (0=day 1), history of therapy or counseling (effect coded −1=nom 1=yes), and gender coded (−1=female, 1=male).
