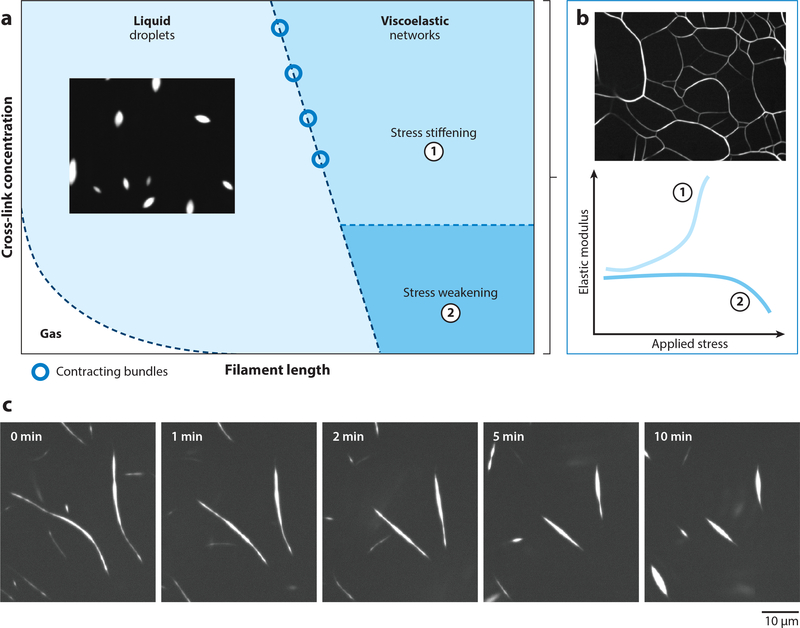
Figure 2.
Materials properties of cross-linked actin networks. (a) State diagram of cross-linked actin networks showing the tunability of mechanical properties by varying cross-link concentration and filament length. When filament lengths are sufficiently long for entanglements, F-actin kinetically arrests to form viscoelastic networks. Short F-actin with sufficiently high cross-linking concentration forms liquid droplets. Gas-like phase appears when both filament length and cross-linking concentration are small. (b) Tunability of elastic modulus of cross-linked F-actin in the viscoelastic phase. F-actin networks stress-stiffen when densely cross-linked and stress-weaken for low cross-linking concentrations. (c) At the boundary between viscoelastic and fluid phases, cross-linked F-actin forms long bundles that contract via surface-tension-like forces. Figure adapted from Reference 53.