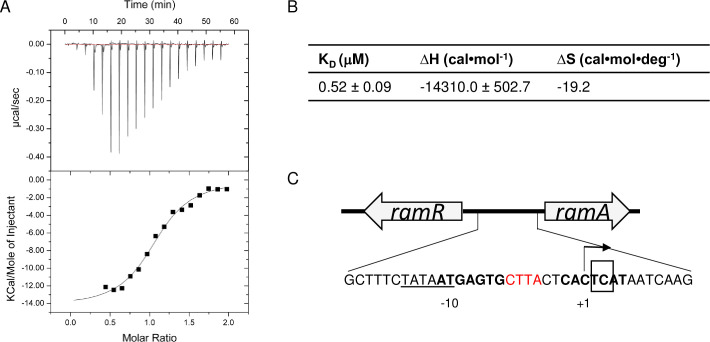
Fig 3. JD1 appears to be a substrate for the AcrAB-TolC efflux pump.
A) Representative ITC for the binding of JD1 to E. coli AcrB. Each peak in the upper panel corresponds to the injection of 2 μL of 100 μM of JD1 in buffer containing 20 mM Na-HEPES (pH7.5), 0.05% DDM and 5% DMSO into the reaction containing 10 μM of E. coli monomeric AcrB in the same buffer. The lower panel shows the cumulative heat of reaction displayed as a function of injection number. The solid line is the least-square fit to the experimental data. B) Kd, enthalpy and entropy of the JD1-AcrB interaction. C) Diagram showing the ramR (ramA repressor) and ramA loci. Bold areas denote where the RamR homodimer binds to repress ramA expression. Base pairs in red are missing in all six JD1-resistant mutant strains. The box indicates the base pair deletion in BN10055 that interferes with RamR binding and increases efflux [47].