Figure 1: Antibody-dependent killing of infected CD4+ T cells is mediated by bNAbs.
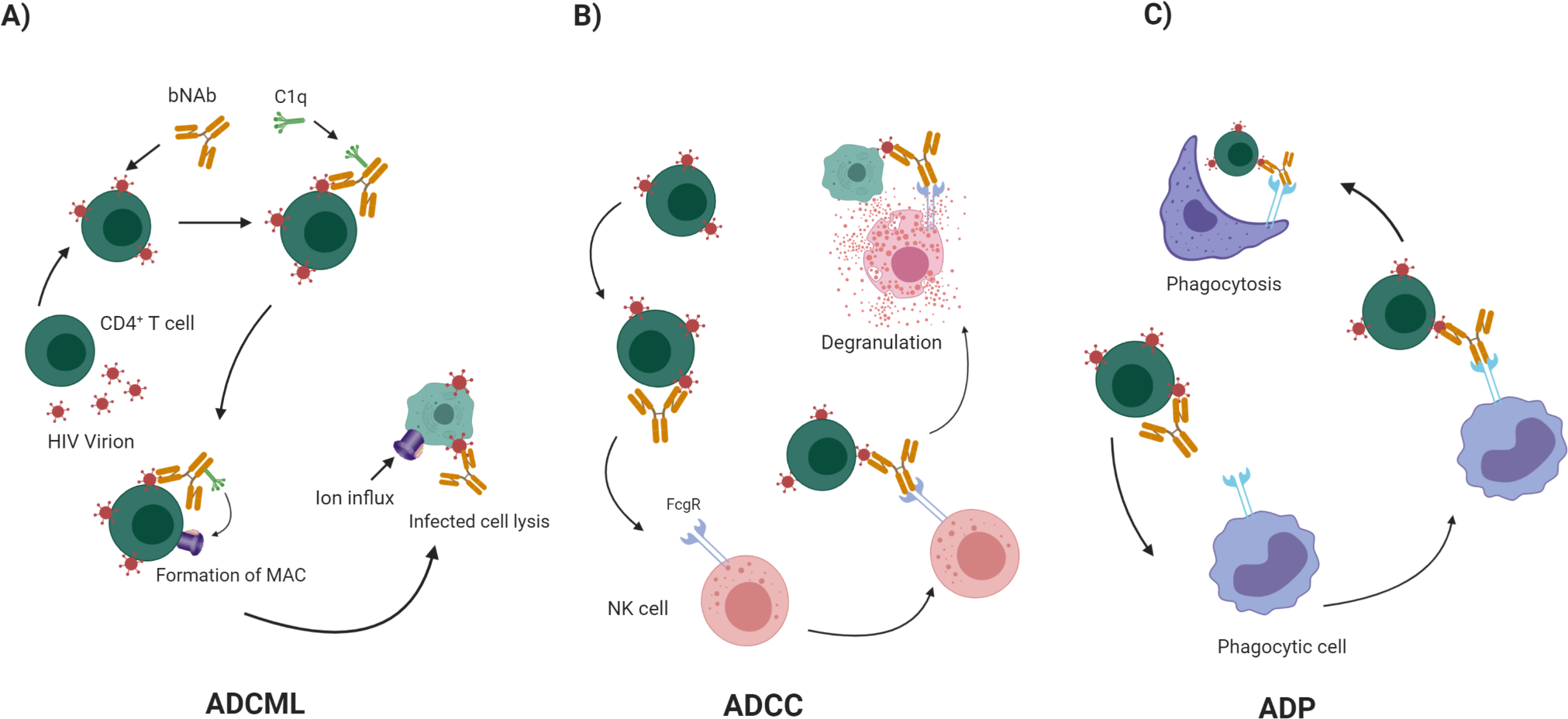
bNAbs initiate several effector functions through their Fc domain. A) Attachment of C1q to the Fc domain of bNAbs that have bound to HIV infected cells initiates the complement cascade, which leads to formation of MAC and lysis of the infected cells by ADCML. B) bNAbs bind to the Env glycoprotein on the surface of HIV-infected CD4+ T cells. NK cells recognize infected cells and bind to Fc domain of the Ab through their FcγR. This binding allows their activation and degranulation, which leads to ADCC killing of the infected cells. B) Professional phagocytes express a diverse set of FcγRs on their surfaces that can bind to bNAb-coated infected cells, deriving them to eliminate infected cells by ADP.
