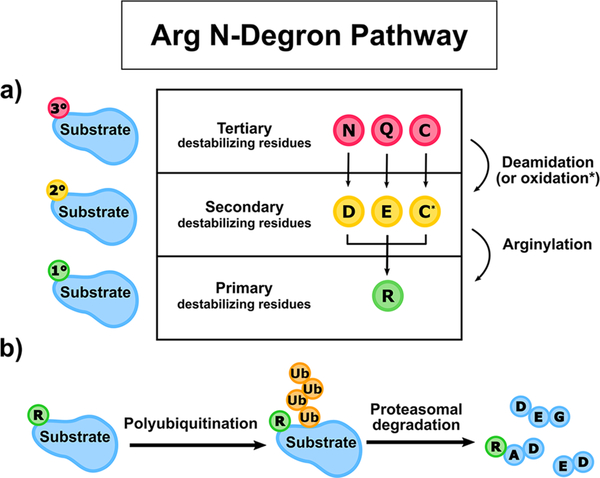
Figure 2.
Cartoon schematic of the Arg N-degron pathway. (a) The hierarchical nature of the Arg N-degron pathway. Tertiary destabilizing residues (red circles) are first either enzymatically deamidated (N or Q) or oxidized (C) to become secondary destabilizing residues (yellow circles). Secondary destabilizing residues (D, E, and oxidized C, denoted C*) are directly recognized by ATE1s, which catalyze the process of arginylation, the nonribosomal conjugation of Arg to a target polypeptide, resulting in the transfer of a primary destabilizing residue (green circles). (b) Arginylation primes a protein substrate for proteolysis. After arginylation, the primary destabilizing residue R (green circle) is recognized by cellular N-recognins, E3 ligases of the ubiquitin-proteasome pathway that ubiquitinate (orange circles) proteins for subsequent proteasomal degradation.