Figure 2.
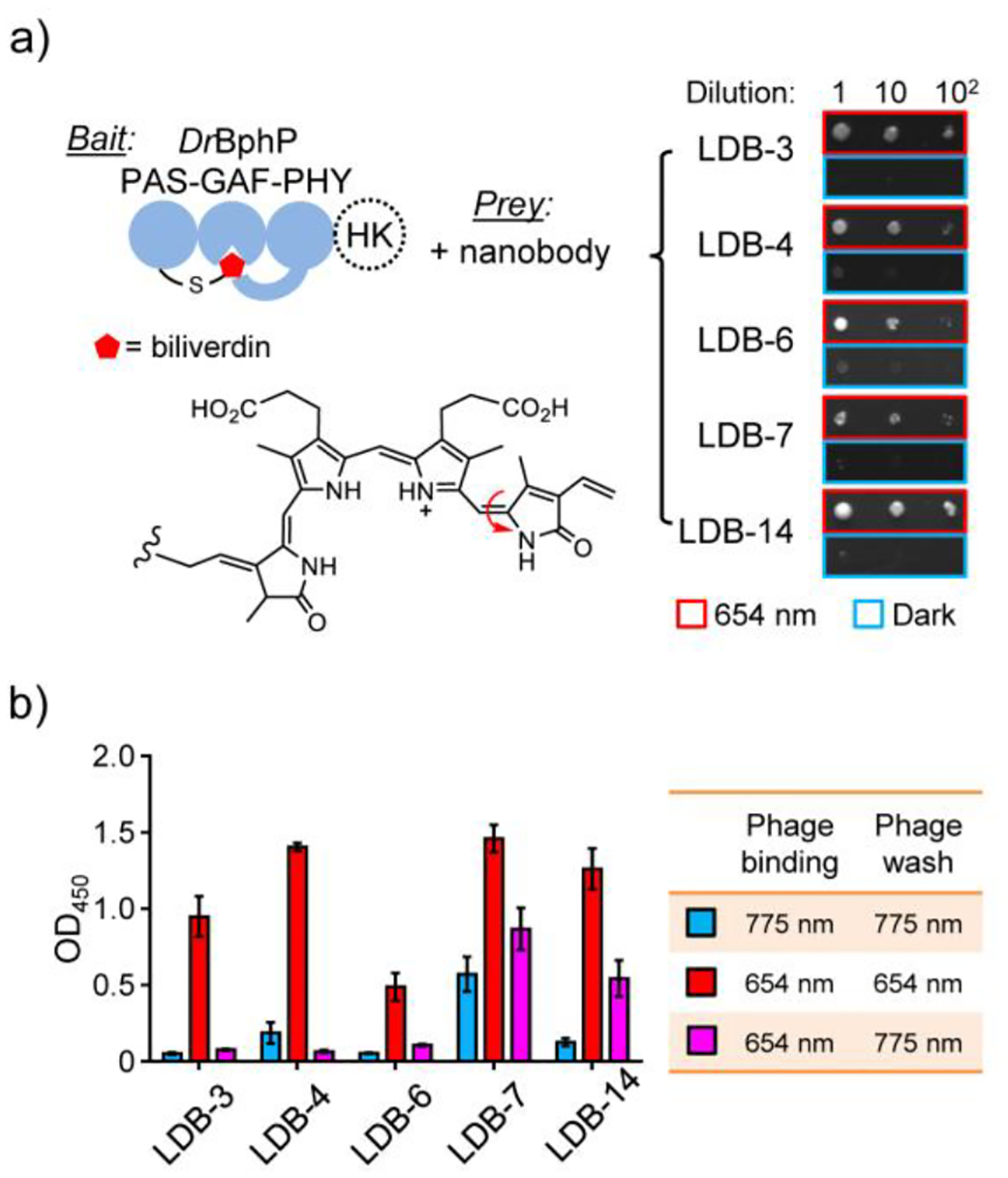
Y2H and single phage ELISA analyses of dimerization binder candidates. a) Y2H assay with the biliverdin-bound DrBphP photosensory module as a bait and nanobodies as preys. The tridomain module was obtained by removing a histidine kinase (HK) domain from the full-length DrBphP. A serial dilution of Y2HGold cells resuspended in 0.9% NaCl were spotted on SD/-Ade/-His/-Leu/-Trp plates (no biliverdin added) and grown under the 654-nm illumination (0.03 mW/cm2) or in the dark. A representative result from three independent experiments is shown on the right. b) ELISA analysis of nanobody binding specificity and reversibility. Phage-displayed nanobodies were bound to DrBphP immobilized in microtiter plates, which were illuminated with the 654-nm (0.3 mW/cm2) or 775-nm (0.2 mW/cm2) lights during the binding and wash steps. Data represent mean values of 3 measurements; error bars, standard deviation.
