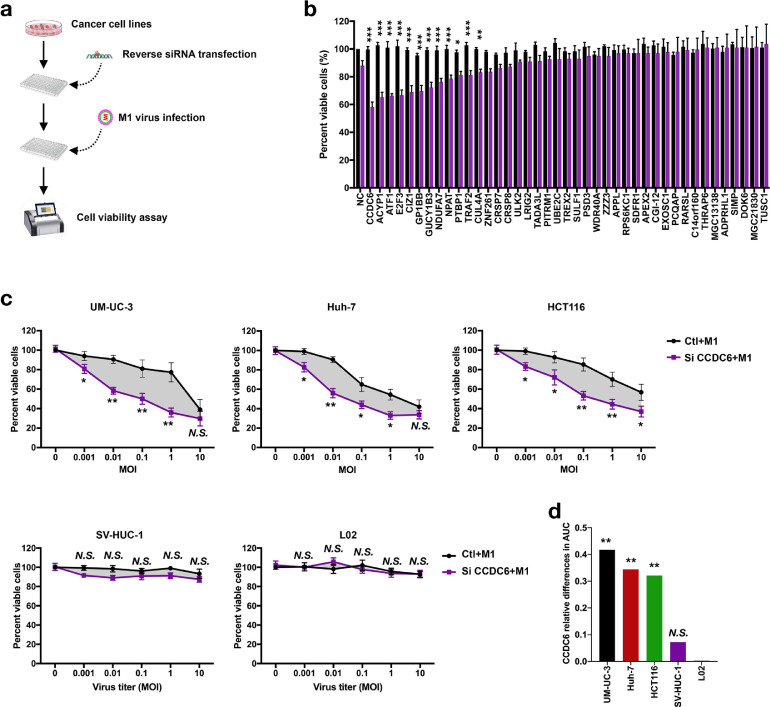
Fig. 2.
Small interfering RNA screen CCDC6 renders tumor cells; however, not normal cells, sensitive to oncolytic virus M1. (a) Schematic of screening strategy to find out CCDC6. (b) UM-UC-3 cells were treated with negative control (NC) or siRNAs for 24 h and then infected with M1 virus (MOI = 1). Cell viability was measured 72 h after the M1 virus infection (n = 3). (c) Tumor cells (UM-UC-3 Huh-7 and HCT116) and normal cells (SV-HUC-1 and L-02) were infected with M1 virus and treated with negative control (NC) or siCCDC6. After 72 h, cell viability was measured (mean ± SD). (d) Bar graphs describe the relative changes in AUC (area under the curve). Ctl, control groups. Data shown in b, c, and d were the mean ± SEM. *P < 0.05; **P < 0.01; ***P < 0.001; N.S., not significant.