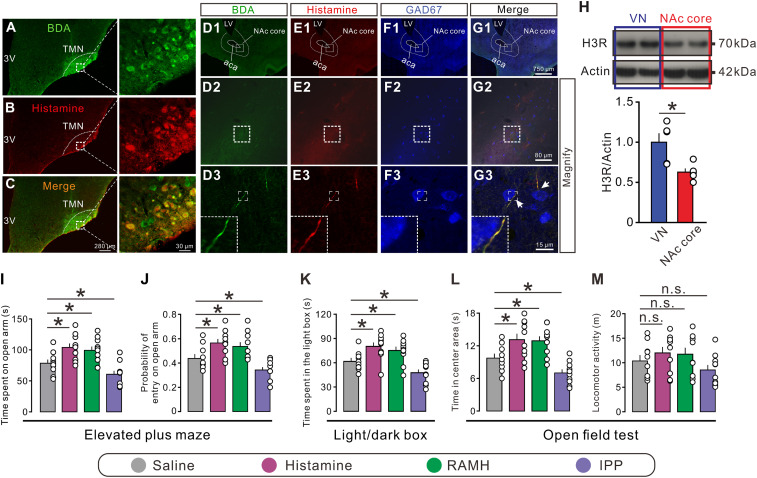
Fig. 1.
Histaminergic afferents in the NAc core and an involvement of the H3 receptor in anxiety-related behaviors. (A–C) Immunostaining micrographs showing the identification of histaminergic neurons with injections of BDA into the TMN. (D1 to G3) Triple immunostaining shows that the anterogradely labeled BDA fibers (green) in the NAc core contain immunoreactivity for histamine (red). Note that these histaminergic fibers pass around GAD67-labeled GABAergic neurons (blue) in the NAc core. LV, lateral ventricle; 3V, third ventricle; aca, anterior commissure, anterior part. (H) Western blot analysis indicates that the histamine H3 receptor is expressed in the NAc core (n = 5). The vestibular nuclei (VN), which have abundant expression of the H3 receptor, were taken as a positive control (n = 5). (I and J) The time and probability of entry into the open arm of rats with bilateral microinjection of saline (n = 10), histamine (n = 10), RAMH (a selective agonist for the H3 receptor, n = 10), and IPP (a selective antagonist for the H3 receptor, n = 10) in the elevated plus maze test. (K) The time spent in the light box of rats with bilateral microinjection of saline (n = 10), histamine (n = 10), RAMH (n = 10), and IPP (n = 10) in the light/dark box test. (L and M) Time in center area and locomotor activity of rats treated by saline (n = 10), histamine (n = 10), RAMH (n = 10), and IPP (n = 10) and in the open field test. Data are shown as means ± SEM; *P < 0.05, n.s., no statistical difference.