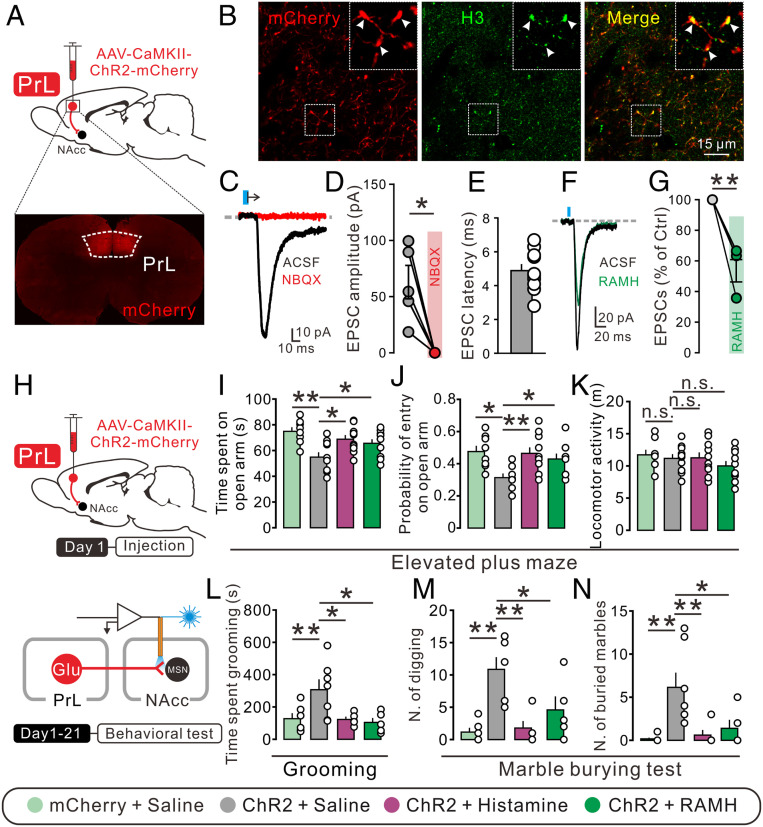
Fig. 5.
Histamine alleviates the anxiogenic and obsessive-compulsive-like behaviors induced by optogenetic activation of the PrL–NAc pathway. (A) Schematics of the optogenetic manipulation of the PrL–NAc glutamatergic pathway and confocal image of ChR2-mcherry expression in the PrL. (B) ChR2-mCherry (red) and H3 receptor (green) expression in the NAc core. (C and D) Bath application of NBQX totally blocked light-evoked EPSCs (n = 5). (E) The latency between light and EPSC onset of the NAc core neurons recorded (n = 10). (F and G) Bath application of RAMH (3 μM) decreased the amplitude of light-evoked EPSCs. (H) Experimental procedure for behavioral test with photoactivation of PrL–NAc glutamatergic terminals. (I–K) The time spent in the open arm, probability of entry into open arms, and locomotor activity of mCherry rats with bilateral microinjection of saline (n = 8), as well as ChR2 rats with bilateral microinjection of saline (n = 10), histamine (n = 10), and RAMH (n = 10). (L–N) The time spent grooming and the number of digging bouts and buried marbles of mCherry rats with bilateral microinjection of saline (n = 6), as well as ChR2 rats with bilateral microinjection of saline (n = 7), histamine (n = 5), and RAMH (n = 5). Data are shown as means ± SEM; *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, n.s., no statistical difference.