Figure 3.
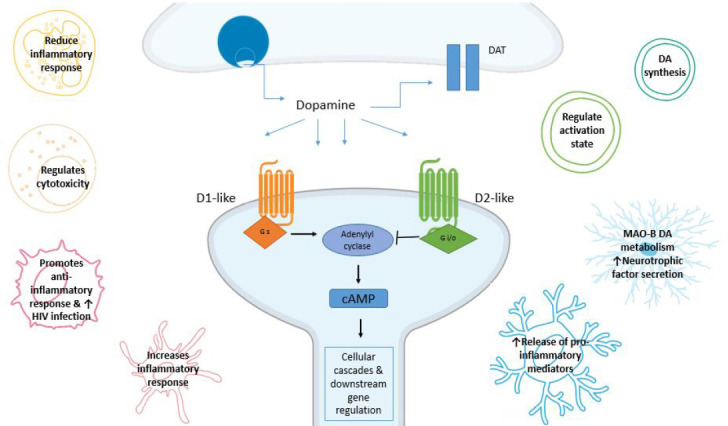
Dopamine receptor (DR) signaling pathways.
DRs belong to the G protein-coupled receptor (GPCR) superfamily and have been divided into two main subclasses, D1-like and D2- like based on their ability to regulate cAMP levels. This figure illustrates the beginning of the neuronal canonical signalling pathway with D1-like receptors activating adenylyl cyclase (AC) and increasing 3',5'-cyclic adenosine monophosphate (cAMP) concentration, while D2-like receptors inhibit AC and consequently reduce cAMP production. We also show how immune cells types have been shown to respond to dopamine (DA). However, limited research is available on how these responses occur. Cells represented include astrocytes (light blue), microglia (dark blue), T lymphocytes (cyan), B lymphocytes (green), neutrophils (yellow), macrophages (pink), dendritic cells (red) and natural killer cells (orange).
