Figure 3.
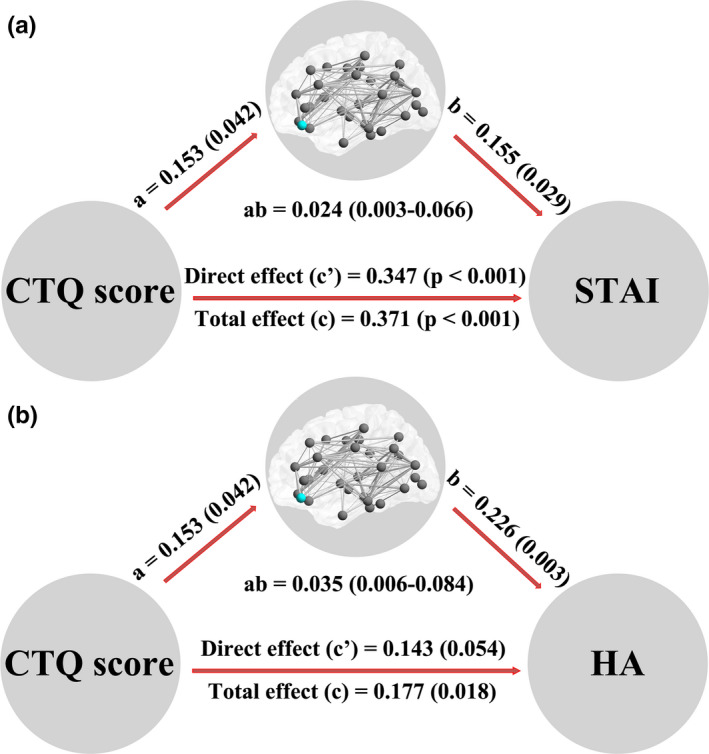
Significant mediation effects in the environment–brain–behavior pathway. We found that efficiency of the right medial OFC within MSN was a significant mediator between CTQ score and STAI/HA. Significant indirect effects were labeled with path coefficients and 95% confidence intervals, while the direct and total effects were labeled with path coefficients and p values. In figure a, there were significant positive effects from CTQ score to STAI score (c = 0.371, c′ = 0.347, p < .001), from CTQ score to efficiency of the right medial OFC (a = 0.153, p = .042), and from efficiency of the right medial OFC to STAI score (b = 0.155, p = .029); the ratio of indirect to total effect was 0.0636. In figure b, there were significant positive effects from CTQ score to harm‐avoiding score (c = 0.177, p = .018), from CTQ score to efficiency of the right medial OFC (a = 0.153, p = .042), and from efficiency of the right medial OFC to harm‐avoiding score (b = 0.226, p = .003); the ratio of indirect to total effect was 0.1945. CTQ: Childhood Trauma Questionnaire; HA: harm avoiding; MSN: morphometric similarity network; OFC: orbitofrontal cortex; STAI: State‐Trait Anxiety Inventory
