Figure 1. Male SHR have greater increases in renal HMGB1 24 h post-IR than females despite comparable injury.
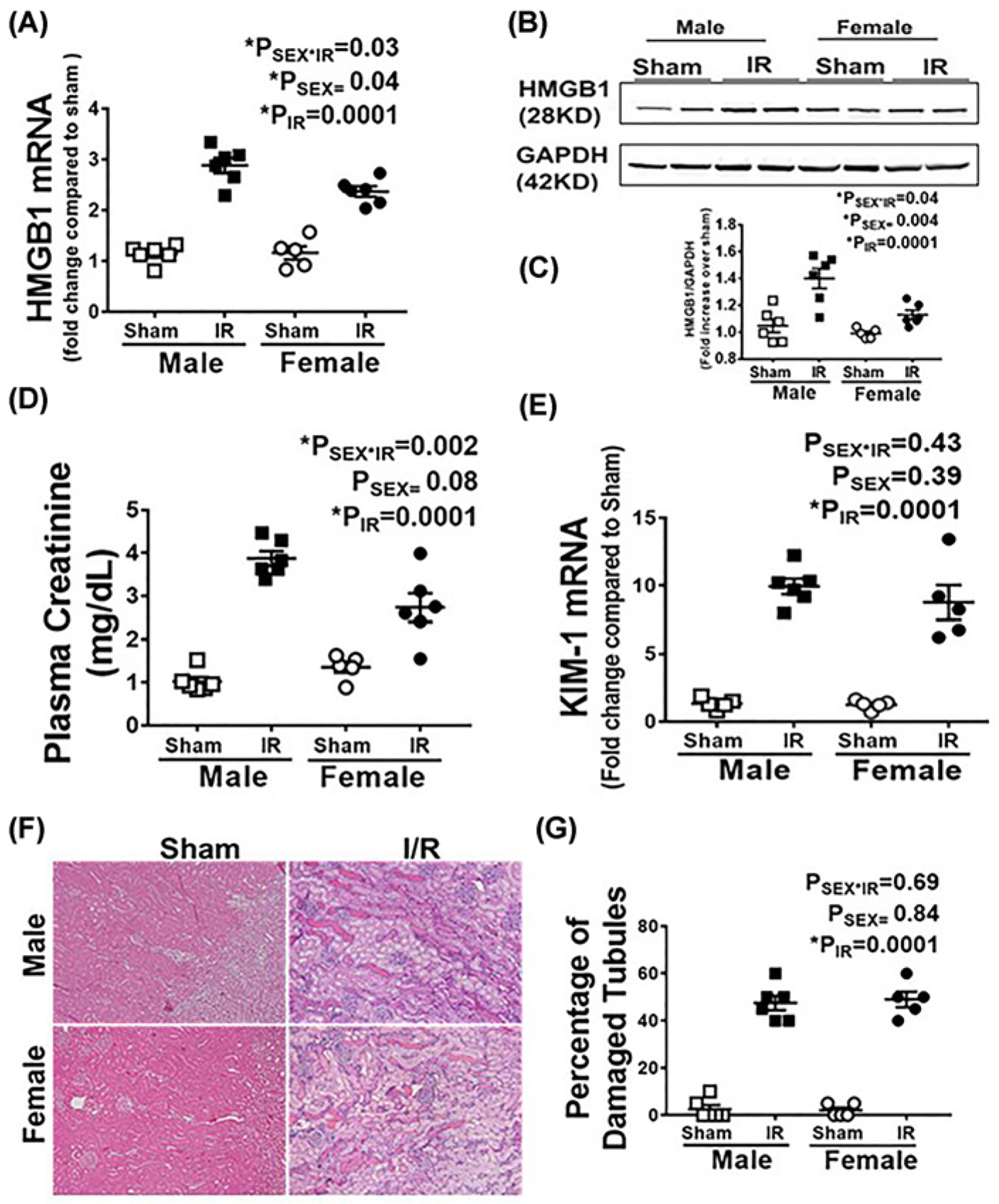
Renal HMGB1 mRNA (A) and protein expression were measured in 13 week old male and female SHR 24 h following sham or 45 min bilateral IR. (B) is a representative Western blot and (C) is the average densitometric analysis. Plasma creatinine (D), renal KIM-1 mRNA levels (E) and tubular damage (F,G) were also measured as indices of renal injury. Representative tubular damage images are shown in (F) (10× magnification, scale bar 200 μM) with the average pathological scoring data in (G). Data are expressed as means ± SEM with individual animal data indicated by the symbols, n=5–6 rats in each group. Open symbols indicate sham animals, filled symbols indicate 45-min ischemia, males are represented by squares and females by circles. Data were compared via two-way ANOVA with P<0.05 considered significant.
