Figure 10.
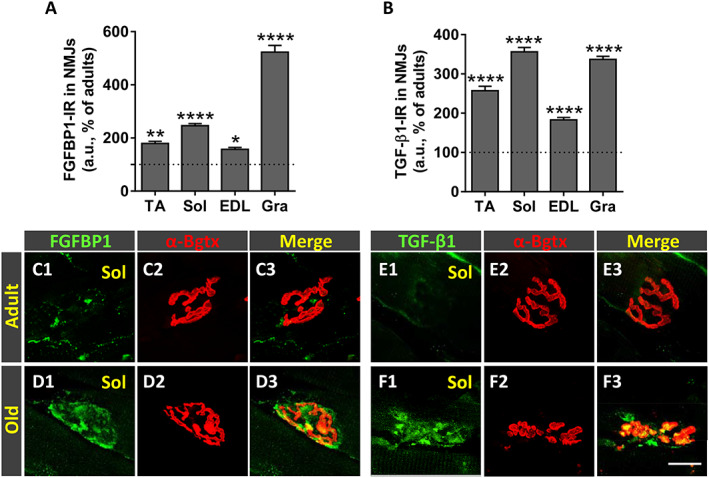
Age‐related changes in fibroblast growth factor binding protein 1 (FGFBP1) and transforming growth factor‐β1 (TGF‐β1) expression in neuromuscular junctions (NMJs) of hindlimb muscles. Quantification of changes in (A) FGFBP1‐immunoreactivity (IR) and (B) TGF‐β1‐IR (in arbitrary units [a.u.]) in NMJs of tibialis anterior (TA), soleus (Sol), extensor digitorum longus (EDL), and gracilis (Gra) muscles of old mice; changes are expressed as the percentage of immunostaining increase compared with adult NMJs. Representative confocal micrographs of NMJs of Sol muscles from adult and old mice immunostained for (C1–D3) FGFBP1 and (E1–F3) TGF‐β1, both in green, as indicated; muscle sections were also stained with α‐bungarotoxin (α‐Bgtx) (red) for endplate identification. Data in the graphs are expressed as the mean ± SEM, * P < 0.05, ** P < 0.01, and **** P < 0.0001 vs. adult muscles (one‐way ANOVA and post hoc Bonferroni's test); one muscle for each muscle type taken from four adult and five old mice was used for analysis; 80–100 NMJs per muscle type were examined. Scale bar in (F3) = 20 μm [valid for (C1–F2)].
