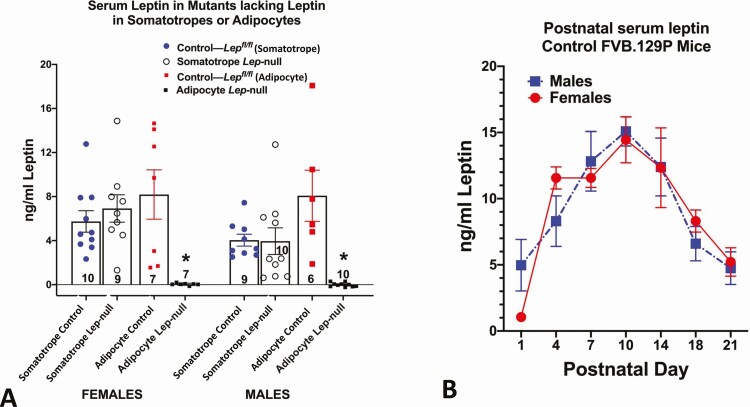
Figure 1.
Serum leptin levels in different physiological states. (A) Serum leptin in mice in which leptin was ablated in somatotropes (Cre-Gh × Lepfl/fl or adipocytes (Cre-Adipoq × Lepfl/fl). Controls for each group are littermates from each line, which bore only floxed leptin (Lepfl/fl). In both females and males, only mice lacking Leptin in adipocytes showed a significant loss in serum leptin (*significantly lower than all other values, ANOVA followed by Tukey’s post hoc test). Method: Serum leptin was assayed by enzyme immunoassay (R&D Systems, Quantikine, MOB00). (B) Sera were collected from male and female FVB.129P mice during neonatal development and assayed for leptin as in Fig. 1A. In both males and females, the peak levels were seen on day 10. Analysis by 2-way ANOVA showed no significant sex differences and a significant postnatal age variance: F = 14.44. DFn = 6, DFd = 64, P < .0001. Tukey’s post hoc test identified significant differences. *Data points that are different from day 1 values. Day 10 values are higher than all others P < .0001) n/age group ranges from 3 to 15 mice.