Fig. 6.
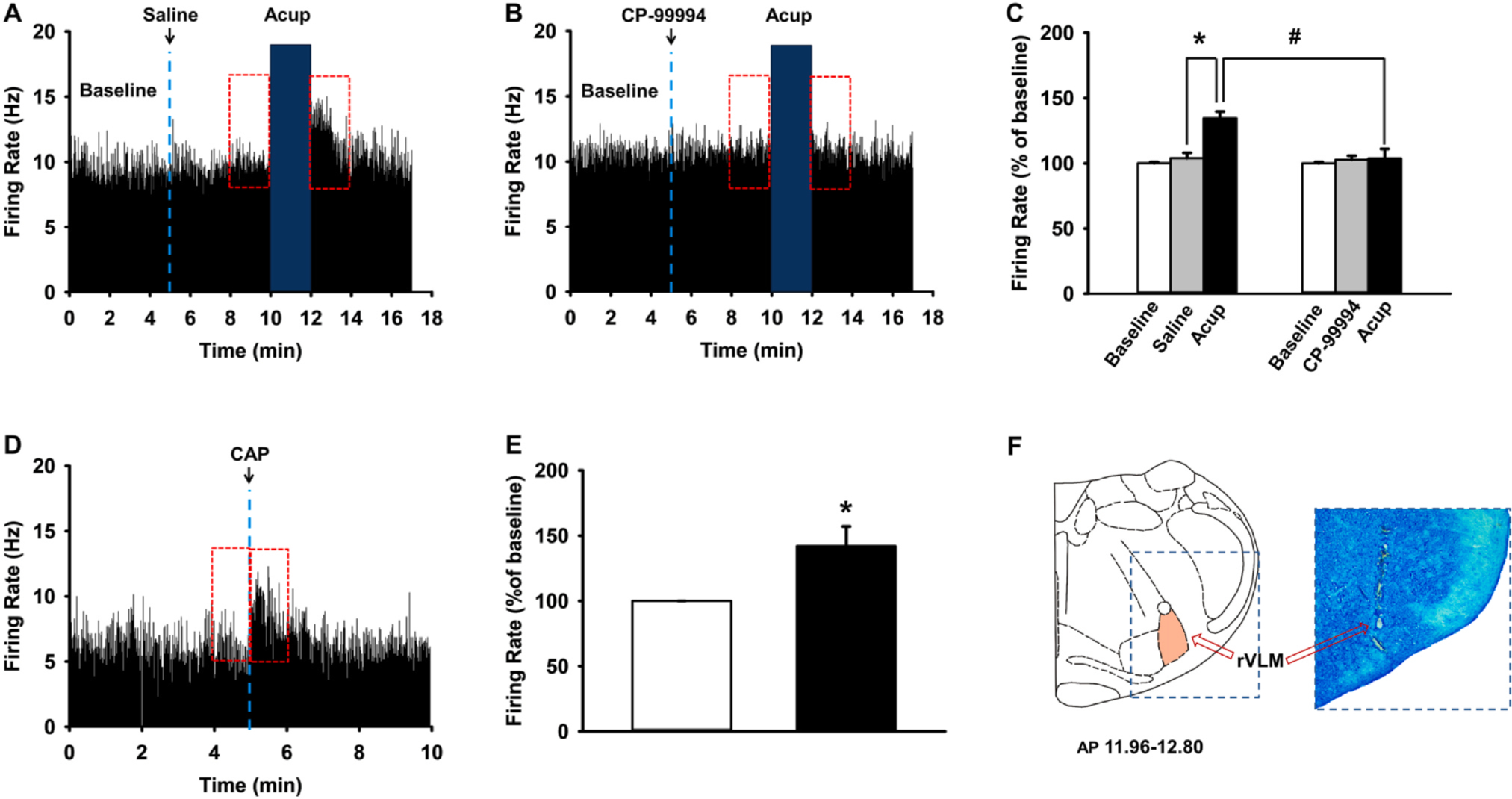
Effect of local injection of an SP receptor antagonist, CP-99994, into Neuro-Sps on responses of rVLM neurons to MAI acupuncture. A-C. Effect of local injection of an SP receptor antagonist, CP-99994, into Neuro-Sps on responses of rVLM neurons to MAI acupuncture. Representative histograms showing rVLM neuronal activity following MAI acupuncture (A) and pretreatment of CP-99994 + MAI acupuncture (B). C. Mean values of firing rates/sec during 2 min after intradermal saline/CP-99994 and MAI at Neuro-Sps, expressed as percentage of the pretreatment values (Baseline). Asterisk * indicates significance level p < 0.05, and hashtag # p < 0.05. MAI stimulation at PC6 near wrist increased the firing rates of rVLM neurons (n = 8; A, C) in IMH rats, while pretreatment of SP receptor antagonist CP-99994 prior to acupuncture prevented acupuncture-induced activation of rVLM neurons in IMH rats (n = 8, B, C). D, E. Effect of intradermal injection of capsaicin into Neuro-Sps on rVLM neuronal activities in normal rats. In vivo extracellular recordings from rVLM neurons (D) and mean values of firing rates/sec during 1 min before and after intradermal injection of capsaicin into the wrist Neuro-Sps, expressed as percentage of the pretreatment values (Baseline) (E). Asterisk *p indicates significance level p < 0.05. F. A representative picture of rVLM lesion stained by toluidine blue.
