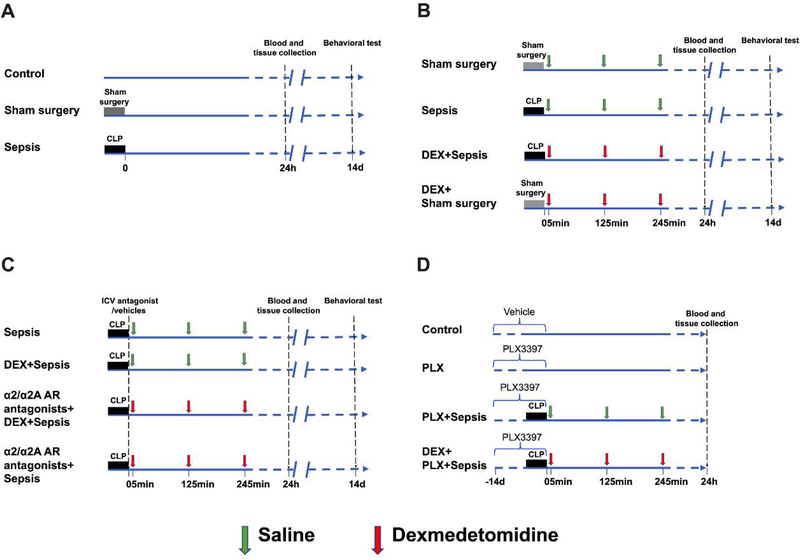
Fig. 1.
Diagram of experiments. (A) Mice were randomly allocated to 3 groups: control, sham surgery and sepsis groups. Blood and tissues were collected at 24 h after cecal ligation and puncture (CLP) or sham surgery. Fourteen days after CLP or sham surgery, Barnes maze and fear conditioning tests were used to determine the learning and memory function of mice. (B) Mice were randomly allocated to 4 groups: sham surgery, sepsis, dexmedetomidine + sham surgery, and dexmedetomidine + sepsis groups. Blood and tissues were collected at 24 h after CLP or sham surgery. Fourteen days after CLP or sham surgery, Barnes maze and fear conditioning tests were used to determine the learning and memory function of mice. (C) Mice were randomly allocated to 4 groups: sepsis, dexmedetomidine + sepsis, intracerebroventricular α2/α2A adrenoceptor antagonists + dexmedetomidine + sepsis and intracerebroventricular α2/α2A adrenoceptor antagonists + sepsis groups. The α2 adrenoceptor antagonist was atipamezole or yohimbine and α2A adrenoceptor antagonist was BRL-44408. Blood and tissues were collected at 24 h after CLP. Fourteen days after CLP or sham surgery, Barnes maze and fear conditioning tests were used to determine the learning and memory function of mice. (D) Mice were randomly allocated to 4 groups: control, PLX3397, PLX3397 + sepsis and dexmedetomidine + PLX3397 + sepsis groups. Blood and tissues were collected at 24 h after CLP. Since harvesting blood and tissues are terminal procedures, the animals for harvesting blood and tissues were a different cohort from those animals used in behavioral testing.