Figure 3.
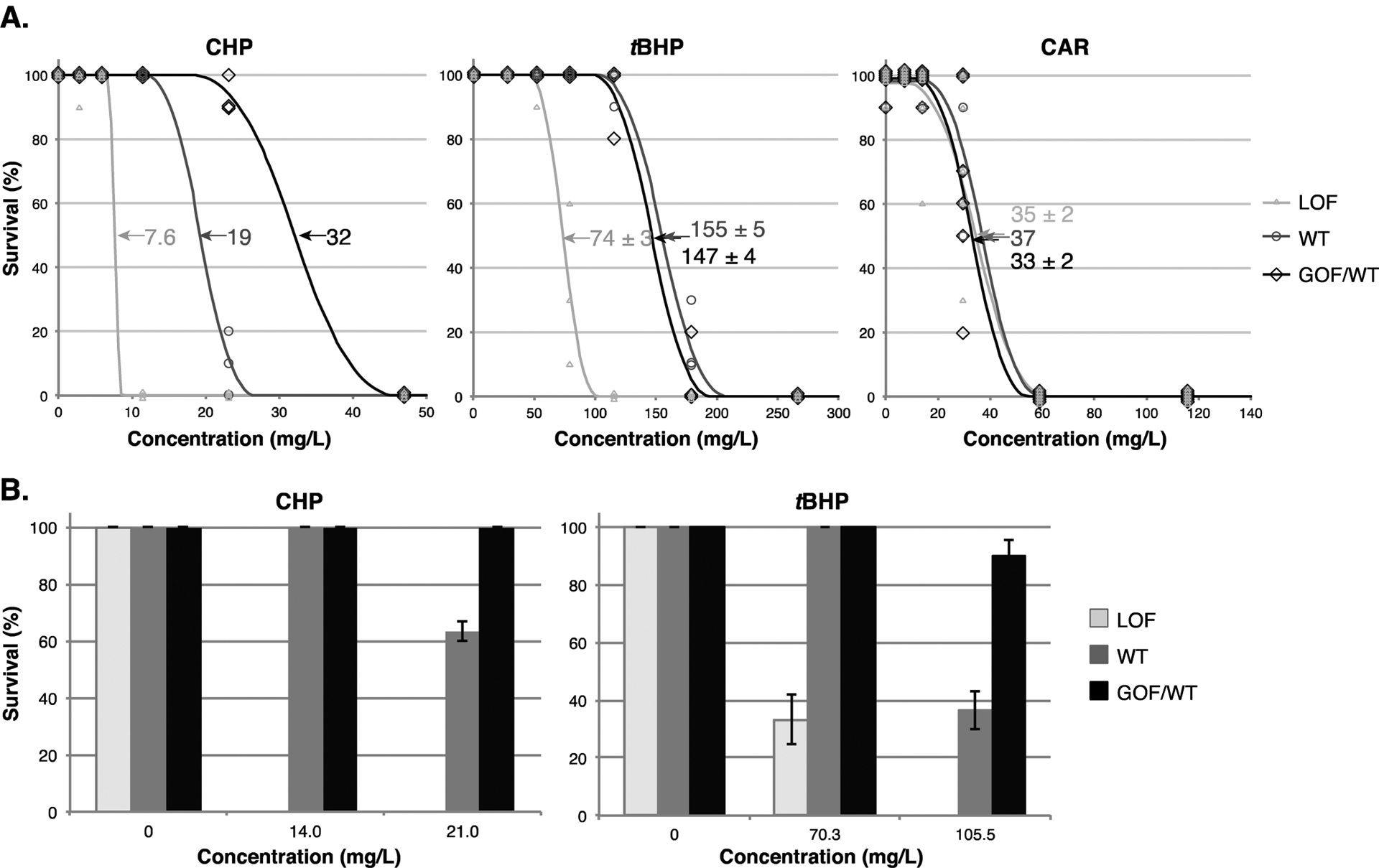
Mutation state of nfe2l2a correlates with chemical toxicity in larvae exposed to CHP and tBHP, but not those exposed to CAR. (a) LC50 exposures between 5 hpf and 96 hpf with daily renewal. Symbols show survival of larvae after exposure to varying concentrations of each chemical; lines show calculated toxicity curves; arrows and numbers indicate calculated LC50 values ± SEM (mg/L). (b) Survival of larvae in exposures starting at 4 dpf to CHP (for 48 h) and tBHP (for 24 h). In all experiments, genotypes are WT (gray), LOF (nfe2l2aw211, light gray), and GOF/WT (heterozygous nfe2l2adw213, black). For CAR, n = 6 biological replicates, 10 fish per replicate; for CHP and tBHP, n = 3 biological replicates, 10 fish per replicate.
