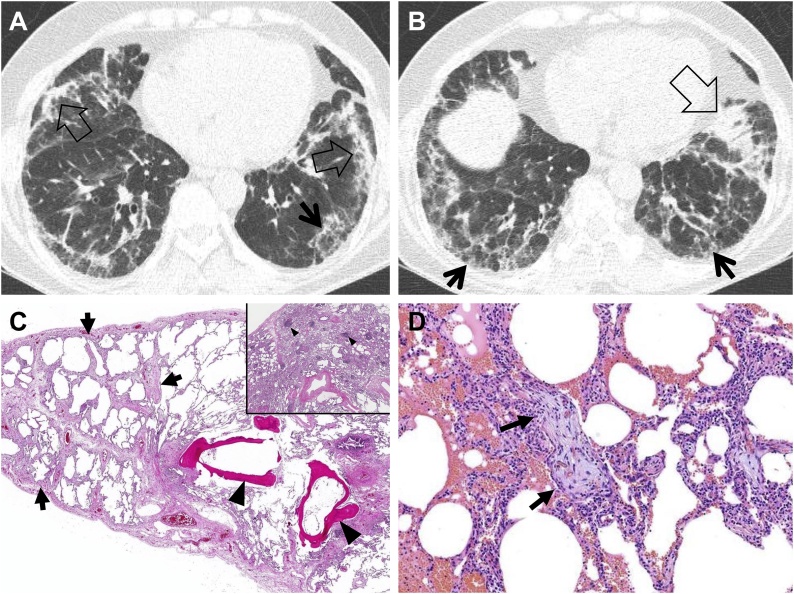
Fig. 3.
Fibrosing organizing pneumonia in a 58-year-old woman with interstitial pneumonia with autoimmune features (IPAF; antineutrophil antibody [ANA], 1:160 and morning stiffness). (a, b) Lung window images of CT scans obtained at levels of cardiac ventricle (a) and liver dome (b), respectively, show patchy distribution of mixed areas of band-like consolidation (open arrows) and reticulation (arrows) in both lungs. (c) Low power magnification of lung demonstrates temporally uniform diffuse lung fibrosis typical of fibrotic NSIP (arrows) associated with dendritic ossification (arrowheads), which is a reflection of chronicity of injury. Inset: Lymphoid follicles containing reactive germinal centers (arrowheads) are randomly scattered in the lung parenchyma suggesting CTD as the underlying cause of the fibrotic NSIP but are not specific. (d) Medium power magnification of lung from the right middle lobe demonstrates organizing pneumonia characterized by airspaces plugs of loose myxoid fibrous tissue (arrows). Organizing pneumonia is a non-specific histologic finding and is one of the lungs most common reactions to injury from any cause.