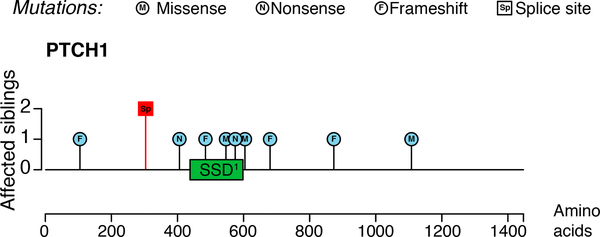
Figure 4: Mapping of the splice site mutation.
Protein level lolliplot of damaging PTCH1 mutations. The left scale indicates the number of siblings affected by each mutation. Somatic mutations were found in BCCs from the two brothers with NBCCS (blue circles). The red box signifies the location of the germline splice site mutation found in both brothers. Most somatic mutations are located close to or within the sterol sensing domain (SSD, green box), which is required for maintaining PTCH1 receptor function. The germline splice site mutation is located before the SSD.