Figure 4.
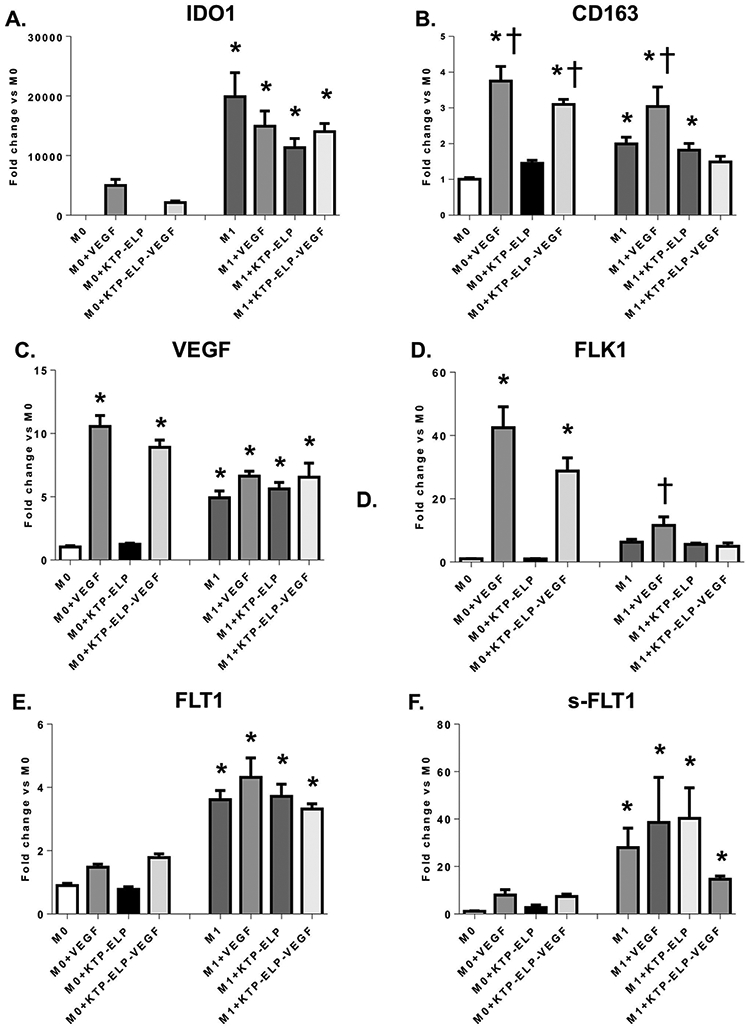
Quantitative real time polymerase chain reaction (qRT-PCR) performed on M0 and M1 macrophages incubated in VEGF, KTP-ELP, KTP-ELP-VEGF, or control media. The macrophage M1 marker (indoleamine-2,3-dioxygenase 1, IDO1, A) was significantly increased in all macrophages incubated in LPS and IFNγ supporting successful M1 polarization. The M2 marker (CD163, B) was dramatically elevated by VEGF or KTP-ELP-VEGF in M0 macrophages indicating that VEGF induces an M2 phenotype primarily through effects on naive macrophages. A significant increase in CD163 was seen in M1s treated with VEGF only, suggesting some phenotype switching from M1 to M2 may occur. M0s showed substantial increases in expression of VEGF (C.) and its receptor Flk-1 (D.) when stimulated with VEGF or KTP-ELP-VEGF, suggesting a feed-forward induction of a pro-angiogenic phenotype. In contrast M1 macrophages expressed moderate levels of VEGF and both membrane-bound (E.) and soluble (F.) forms of its receptor Flt-1 at baseline but showed no demonstrable response to VEGF therapy. n=6 per group. *p<0.05 vs. M0 † p<0.05 vs. M1 (Single way ANOVA, Tukey).
