Figure 3. Effects of HIV and a history of METH dependence on PPI in male participants.
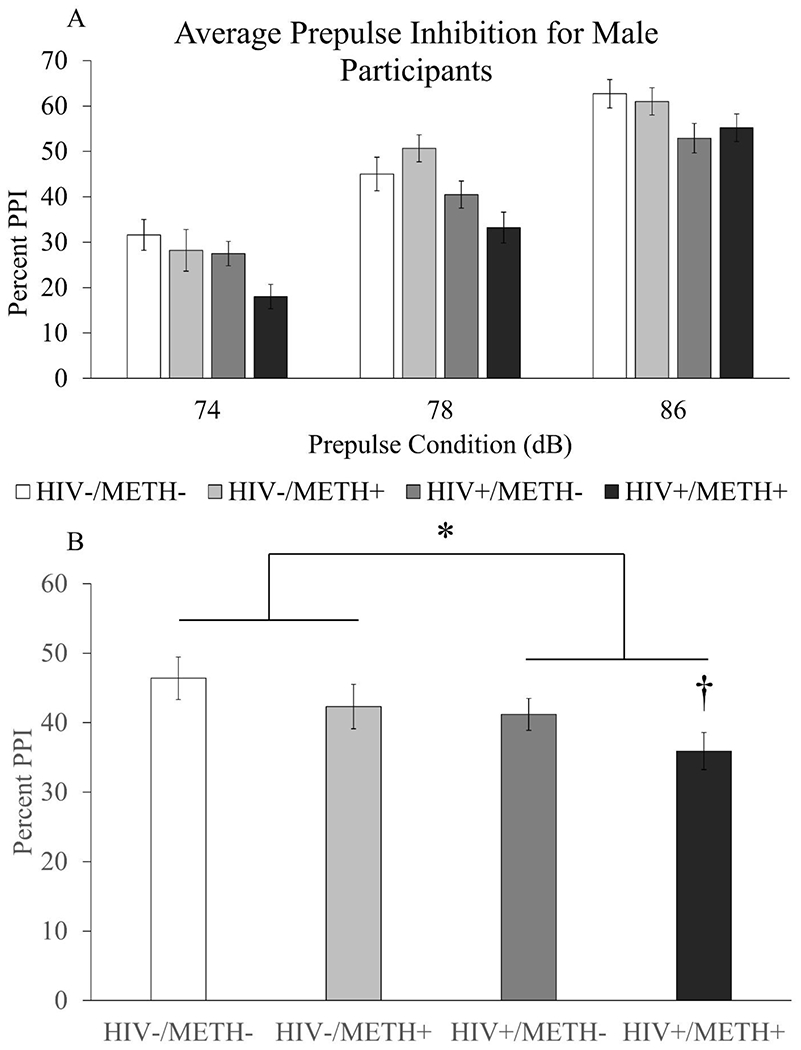
Four groups of human men with or without HIV and with or without a history of METH dependence (HIV−/METH−: n=42, HIV−/METH+: n=29, HIV+/METH−: n=47, HIV+/METH+: n=42) were recruited and assessed for PPI at three different prepulse intensities. Average PPI for each group at each prepulse intensity are shown in panel A. PPI averaged across prepulse intensities are shown in panel B. Data are presented as mean ± S.E.M. * = main effect of HIV (Two-way ANOVA, p=0.003); † = significantly different compared to HIV−/METH− group (p=0.019, Dunnett’s posthoc test).
