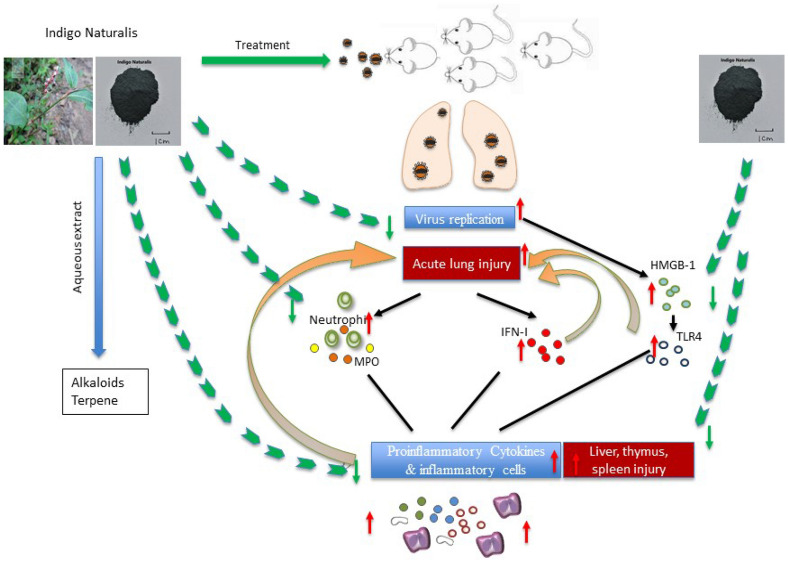
Fig. 9.
Graphic abstract of IAV-induced acute lung injury. Influenza A virus infected host alveolar epithelial cells and caused necrosis and injury in lung. The innate immune response began with the virus recognition and was amplified through activation of HMGB-1 and TLR4 signaling pathway. Extensive production of cytokines, chemokines produced by inflammation cells and amounts of peroxide products released from neutrophils exacerbated the injury of lung and multi organ failure in liver, thymus and spleen (red arrow). INAE treatment alleviated the acute lung injury and multi organ damage (green arrow) through the effects of anti-virus, anti-inflammatory and anti-oxidation