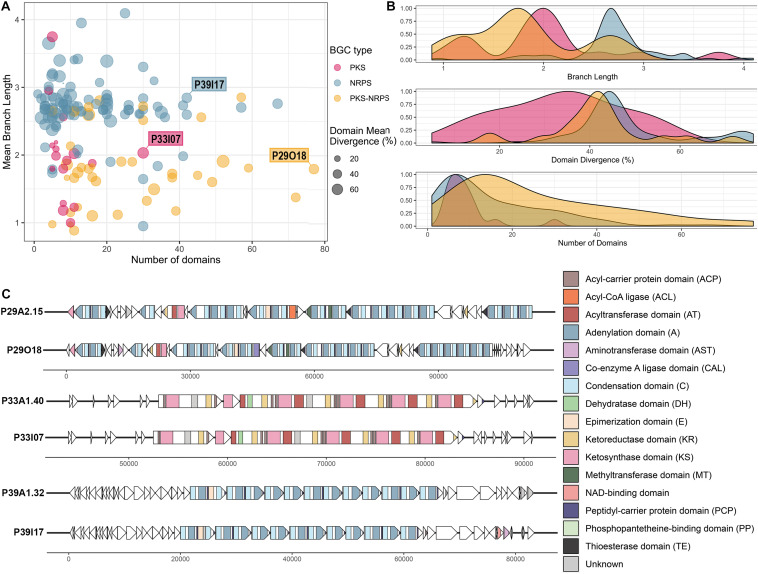
FIGURE 5.
Analysis of the clones containing viable PKS and NRPS pathways reconstructed and validated from the Cullars metagenomic library. (A) Viable PKS and/or NRPS clusters recovered from the library compared by size (number of domains) and divergence from known BGCs (mean branch length and domain mean divergence). Each plot point represents a clone containing a viable BGC. Mean branch length for each clone is calculated as the average branch length of all the clones’ KS and/or A domains, as extracted from the ML trees against the MIBiG database. Mean domain divergence for each clone is calculated as the average domain divergence of all clones’ KS and/or A domains. Domain divergence is the complementary percentage to the% identity of the domain to the NCBI nr database (if a domain has% identity of 60, then the domain divergence is 40%). (B) Density distribution of branch length, domain divergence and number of domains across the viable PKS and NRPS BGCs. (C) Annotation of three interesting representative BGCs, representing the longest BGC from each type (PKS, NRPS, PKS-NRPS) to be recovered successfully in silico from the metagenomic library NGS contigs and validated upon clone resequencing. Annotation from the library contig was compared to the annotation from their corresponding validated insert sequence. ORFs are depicted by arrows and the PKS and/or NRPS domains within each ORF are represented by colored stripes.