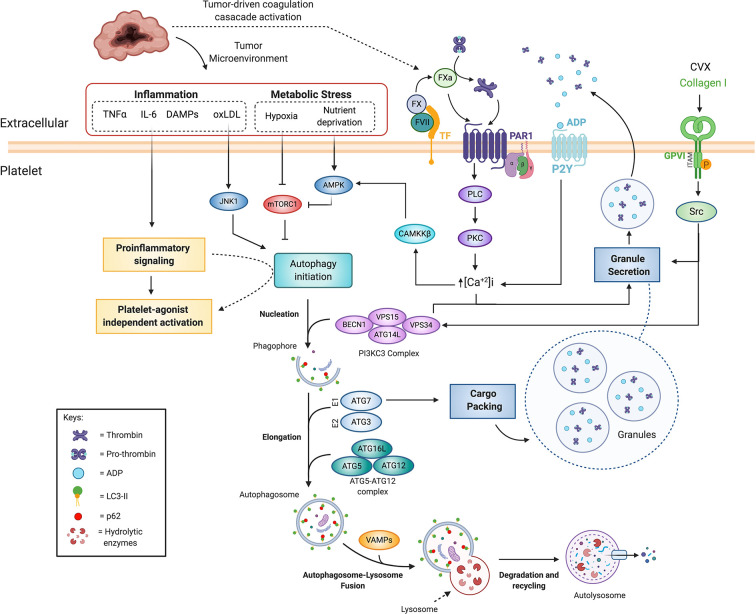
Figure 4.
Coagulation cascade and autophagy crosstalk in platelet activation and cancer-associated thrombosis. Platelet agonists such as thrombin, ADP and collagen can increase autophagic flux, which is necessary for efficient platelet activation. PAR activation and P2Y engagement activate the PLC-PKC-Ca2+ signaling, which has been shown to increase platelet autophagic flux during platelet activation, possibly through CAMKKB. Additionally, autophagy proteins such as BCN1, VPS34, ATG7, ATG5, and VAMPs have been shown to be necessary for platelet activation, cargo packing and granule secretion. Tumors increase systemic inflammation and locally generate both hypoxia and nutrient deprivation, which cannot only promote platelet activation but also autophagy through JNK and AMPK activation, and mTORC1 inhibition. Pro-inflammatory signaling through increased levels of extracellular TNFα, IL-6, and IL-8, which are frequently elevated in cancer patient serum samples, is involved in both platelet activation and possibly modulating platelet autophagy. ADP, adenosine diphosphate; AMPK, AMP-activated protein kinase; ATG, autophagy-related proteins; BECN1, Beclin-1; CAMKKB, calcium/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase kinase 2; CVX, convulxin; DAMPs, Damage-Associated Molecular Patterns; FVII, Factor VII; FX, Factor X; FXa, activated FX; GPVI, Glycoprotein VI; IL-6, Interleukin 6; IL-8, Interleukin 8; JNK1, c-Jun N-terminal kinase 1; LC3, microtubule-associated protein 1A/1B-light chain 3; mTORC1, mammalian target of rapamycin complex 1; oxLDL, Oxidized low-density lipoprotein; PAR, protease activated receptor; PE, phosphatidylethanolamine; PI3K, phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase; PKC, Protein kinase C; PLC, Phospholipase C; TF,Tissue Factor; TNFα, Tumor Necrosis Factor α; VPS, vacuolar protein sorting; VAMP, Vesicle associated membrane proteins.