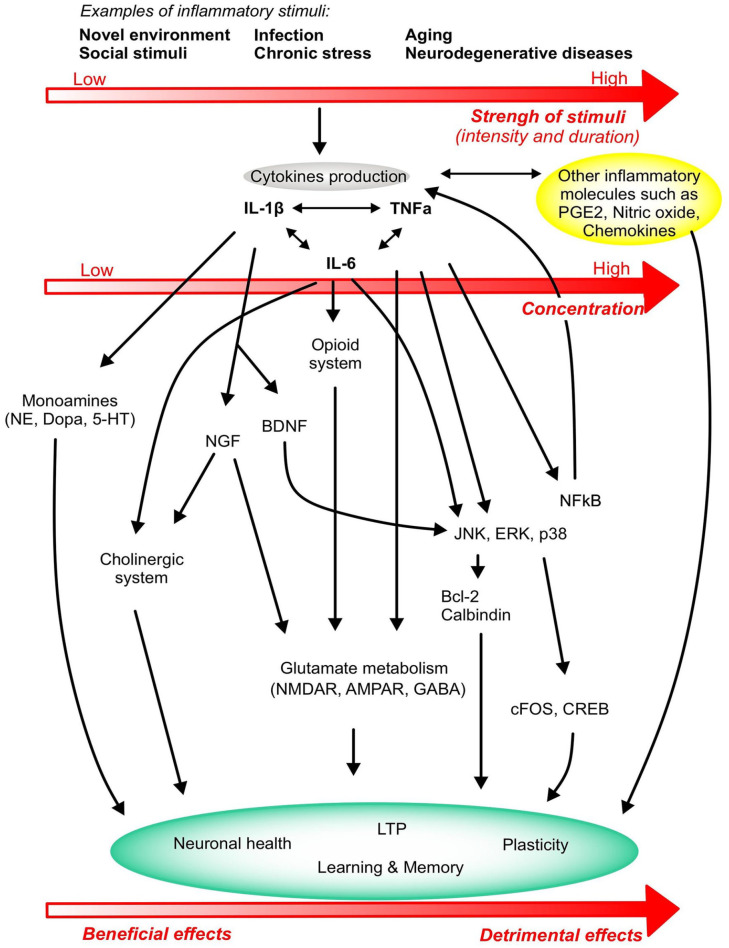
Figure 2.
Overview of the major mechanisms of action of cytokines on plasticity and learning and memory. Stimuli of different intensity and duration activate the production of cytokines IL-1β, TNF-α and IL-6 that in turn modulate several metabolic and molecular pathways, ultimately affecting neurocircuits that regulate learning and memory function. The strength and duration of the stimulus determine the concentration and production levels of cytokines, leading the cytokine response to generate either beneficial effects on learning and memory or detrimental effects that ultimately progress towards neuronal death and cognitive deficits. Cytokine production also activates other inflammatory systems like PGE2, nitric oxide and other chemokines that will impact on the inflammatory status of the brain and the learning, memory and plasticity responses.