FIGURE 1.
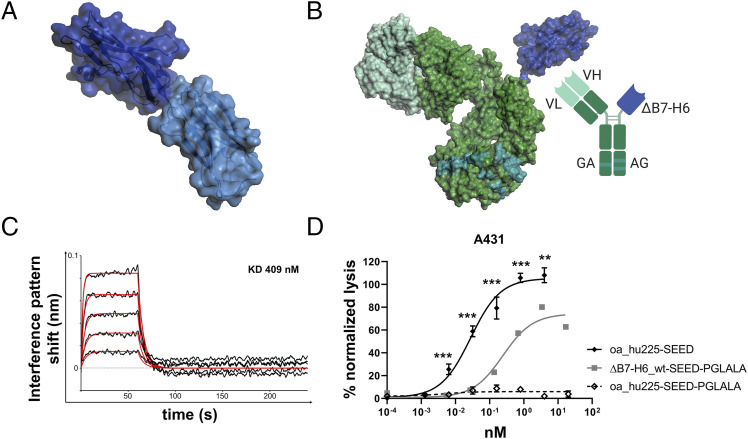
B7-H6 IgV domain is sufficient to elicit NK cell–mediated tumor cell lysis. (A) Structure of the extracellular domain of B7-H6 with N-terminal IgV domain colored in dark blue and the IgC part depicted in light blue. Model based on pdb entry 3pv7 and was generated with PyMOL v0.99. (B) Structural model (left) and scheme (right) of generated immunoligands for NK cell redirection consisting of ΔB7-H6 (dark blue) and the humanized Fab of cetuximab (hu225) in an effector-silenced IgG1 SEED backbone comprising amino acid exchanges L234A, L235A, P329G. The V region H chain and L chain are colored in green-cyan, Ab backbone in green, SEED GA and AG in CH3 domains indicated by deep teal coloring. Model based on pdb entries 5dk3 and 3pv7 and constructed using PyMOL v0.99. Scheme generated with BioRender (http://www.biorender.com). (C) Biolayer interferometry analysis of wild-type (wt) ΔB7-H6 immunoligand binding to NKp30. (D) Killing property of ΔB7H6_wt-SEED-PGLALA (solid square) was compared with oa hu225-SEED activating FcγRIIIa (solid diamond) and Fc-silenced oa_hu225-SEED-PGLALA lacking the B7-H6 IgV domain (open diamond) as a control molecule in standard 4-h 51Cr release experiments using freshly isolated human NK cells of healthy donors and A431 tumor cells in an E:T ratio of 10:1. Normalized percentage tumor cell lysis of three independent experiments with different donors is shown as mean ± SEM. ***p < 0.001, **p < 0.01 of oa_hu225-SEED versus ΔB7-H6-SEED-PGLALA.