Figure 3.
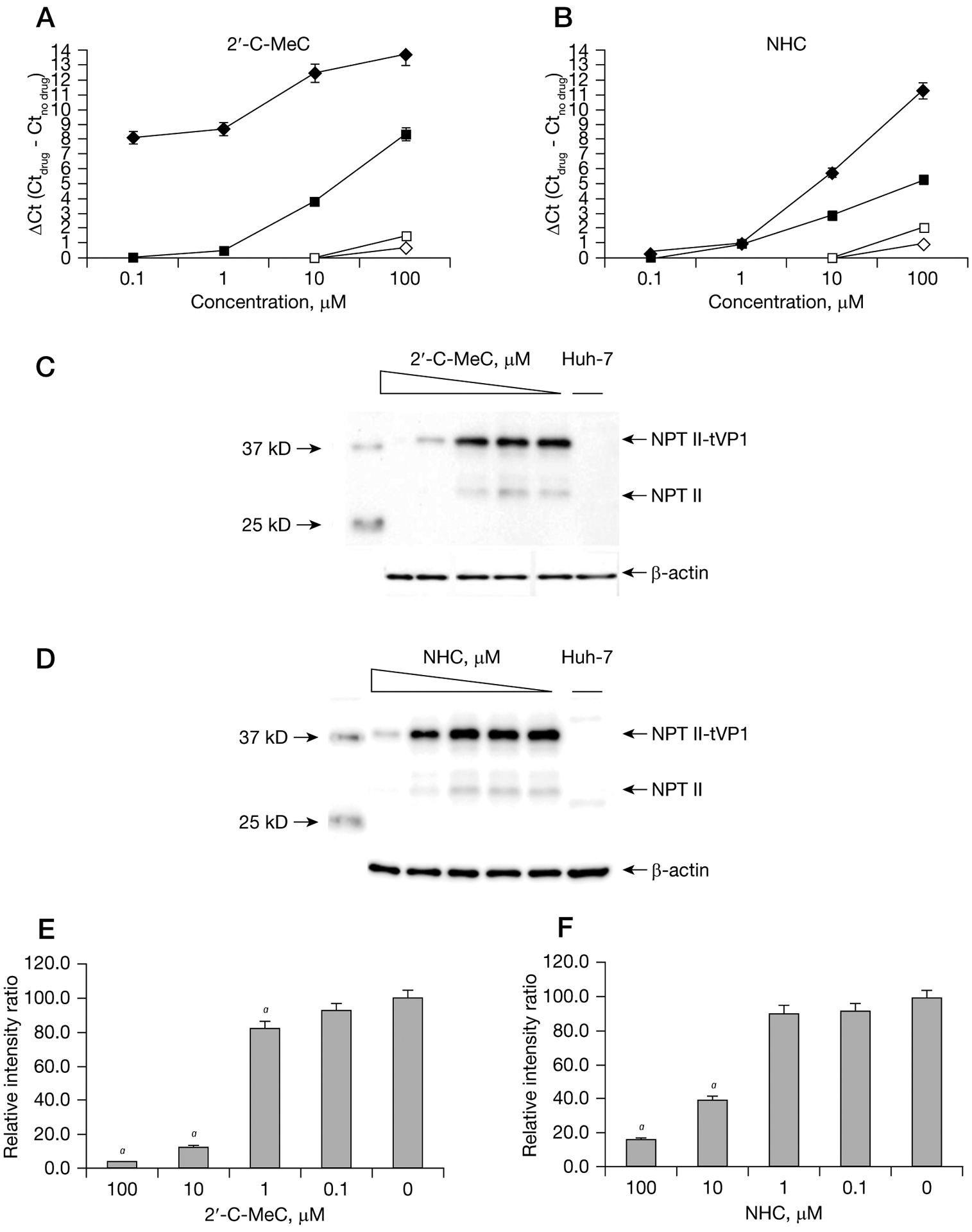
Single compound dose- and time response curves for inhibition of NV replication in HG23 cells
One-day-old semiconfluent HG23 cells were incubated with increasing concentrations (0.1 μM to 100 μM) of each nucleoside. Reduction of Norwalk virus (NV) RNA levels at 24 h (represented by an open diamond), 48 h (represented by an open square), 72 h (represented by a black square) and 96 h (represented by a black diamond) after treatment with (A) 2′-C-MeC or (B) β-D-N(4)-hydroxycytidine (NHC) were quantified by RT-qPCR. To express antiviral effectiveness, the mean Ct value of the no-drug control cells (Ctno drug) was subtracted from the mean Ct value from treated wells (Ctdrug). A ΔCt of 3.3 equals 1-log reduction in norovirus RNA levels (90% effective concentration). Each point represents the mean ± standard deviation of three replicate experiments (antiviral treatment) and three independent RT-qPCR runs. Effect of (C) 2′-C-MeC or (D) NHC on the expression of neomycin phosphotransferase II (NPT II) detected by western blot analysis after 72 h incubation. Expression of NPT II and NPT-II fused to truncated VP1 (NPT II-tVP1) was measured as previously described [13,17]. Huh-7 cells were included as negative control for NPT II expression. Band intensities were normalized against β-actin and expressed as a percentage of the untreated HG23 cells intensity. aNPT II levels for cells treated with (E) 2′-C-MeC (F) or NHC that were significantly (P<0.001) different from cells without treatment.
