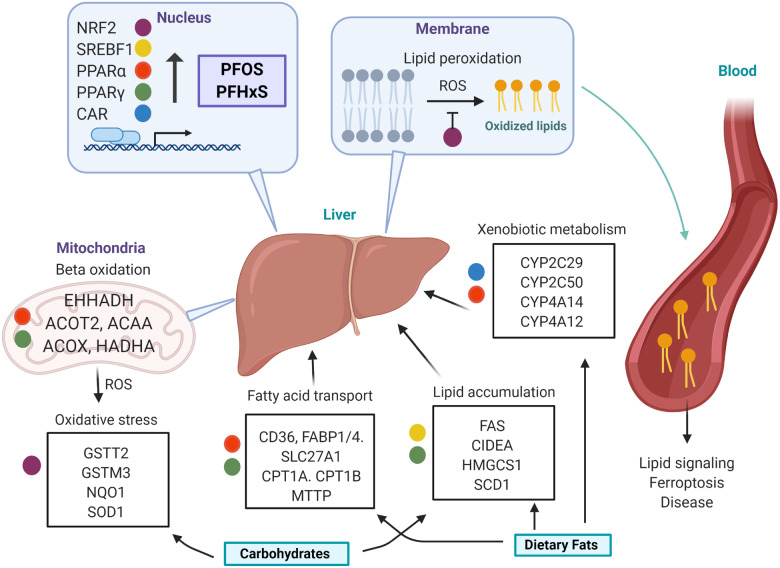
Figure 9.
Proposed hepatic mechanism of PFOS and PFHxS modulation of the blood lipidome. PFOS and PFHxS activate transcriptional drivers that modulate hepatic pathways involved in lipid accumulation, fatty acid beta oxidation, lipid transport, xenobiotic metabolism, and oxidative stress. A high-fat high-carbohydrate (HFHC) diet potentiates fatty acid accumulation and metabolism, as well as, oxidative stress. Reactive oxygen species (ROS) initiate lipid peroxidation in the phospholipid bilayer, resulting in an efflux of oxidized lipid species to the blood. These oxidized lipids act as signaling molecules may be associated with adverse health outcomes.