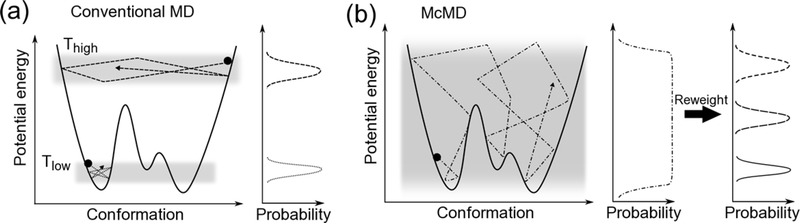
Figure 1.
Schematic view of conformational space and potential energy. Filled circles indicate initial structures. (a) Conventional MD performed at low temperature would be trapped at a local minimum and could not overcome the large potential energy barrier. High temperature MD samples a wider conformational space and overcomes large barriers; however, the structures are unrealistic. (b) McMD can equally sample a full potential energy space, easily overcome large barriers, and sample any local minima. Therefore, the staring conformation does not affect the results. After a production McMD run, canonical ensembles between low and high temperature states are easily obtained by reweighting.