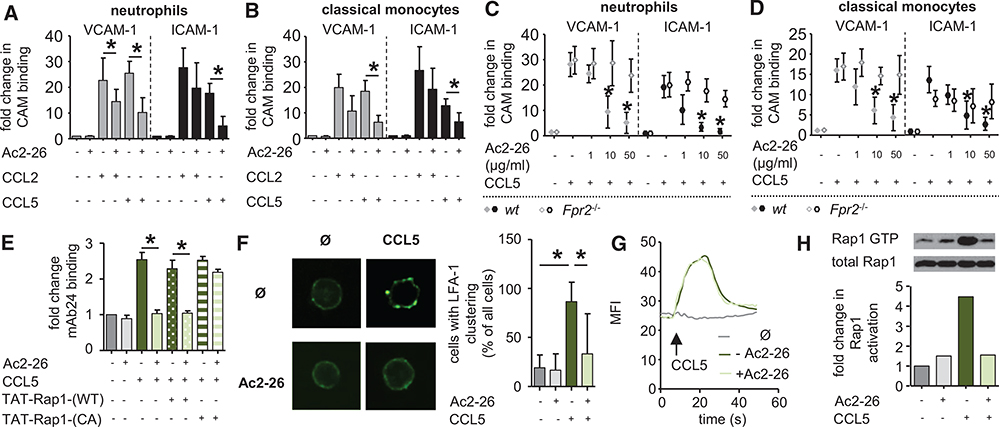
Figure 4. Annexin A1 counteracts chemokine-induced integrin activation.
A and B, Annexin A1 inhibits chemokine-evoked integrin activation on myeloid cells. Neutrophils (A) and classical monocytes (B) from C57Bl/6 mice were treated with CCL2 or CCL5, and binding of soluble vascular cell adhesion molecule-1 (VCAM-1)-Fc or ICAM-1-Fc was assessed by flow cytometry. Effect of Ac2-26 was determined by pretreatment for 30 minutes before chemokine stimulation. C and D, Dose-dependent response of Ac2-26 on CCL5-evoked binding of VCAM-1-Fc or intercellular adhesion molecule-1 (ICAM-1)-Fc on neutrophils (C) and monocytes (D) harvested from C57Bl/6 (wild-type [WT]) or Fpr2−/− mice. E, β2 integrin activation assessed by mAb24 binding and flow cytometry in human neutrophils incubated with CCL5 and preincubated with Ac2-26. Where indicated, neutrophils were pretreated with WT or constitutively active (CA) Rap1-Tat peptides. F, Redistribution of surface LFA1 on mouse neutrophils stimulated for 90 s with CCL5 and pretreated for 30 minutes with Ac2-26. G, Mean fluorescence intensity (MFI) reflecting intracellular calcium in mouse neutrophils before and after addition of CCL5 with or without Ac2-26, which was added 30 minutes before CCL5 stimulation. Data are representative recordings from 5 independent runs. H, GTP-bound Rap1 protein in mouse neutrophils 30 s after stimulation with CCL5 and prestimulation for 30 minutes with Ac2-26. Representative blots from 3 experiments are shown. All data are presented as mean±SD. Experiments were performed ≥6× independently for A–E. *P<0.05 in C and D *Differences compared with CCL5 stimulation. Data were analyzed using Kruskal–Wallis test with Dunn post test. CAM indicates cell adhesion molecule.