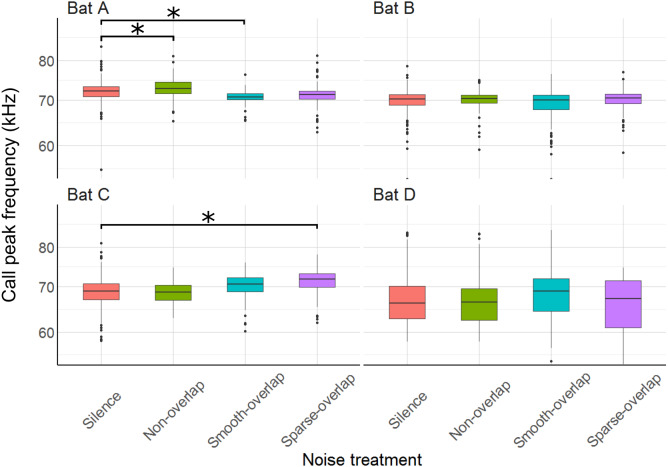
Figure 8. Peak frequency of echolocation calls during the discrimination tasks by noise treatment.
Peak frequency of bat A increased under smooth non-overlapping noise and decreased under smooth overlapping noise. Peak frequency of bat C increased under sparse-overlapping noise. Box plots show median (solid line) and first and third quartiles (edges of box); whiskers extend to the rest of the data minus outliers (more than 1.5 times the interquartile range), which are shown as points. Noise treatments have been abbreviated here (as compared to the text) to reduce visual clutter (smooth non-overlapping noise = “Non-overlap” here; smooth-overlapping noise = “Smooth-overlap” here; sparse-overlapping noise = “Sparse-overlap” here). Asterisks denote significant differences (p < 0.05) relative to the control treatment.