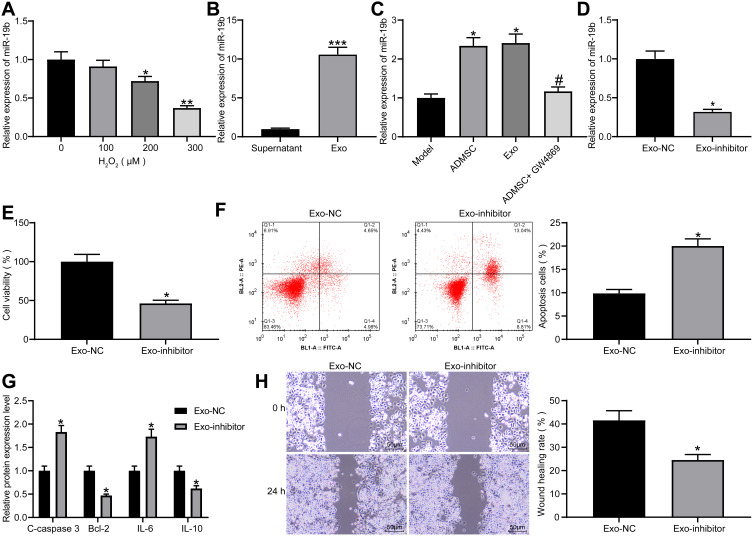
Figure 4.
Exosomal miR-19b alleviates H2O2-induced HaCaT cell damage. (A) RT-qPCR was conducted to determine miR-19b expression in HaCaT cells treated with different concentrations of H2O2 (one-way ANOVA, *P < 0.05 or **P < 0.01 vs 0 µM). (B) RT-qPCR was carried out to detect miR-19b expression in supernatant and exosomes (unpaired t test, ***P < 0.001). (C) RT-qPCR was performed to detect miR-19b expression in Transwell co-culture system (one-way ANOVA, *P < 0.05 vs the model group; # P < 0.05 vs ADMSCs group). (D) RT-qPCR was conducted to determine miR-19b expression in ADMSCs-derived exosomes that had been transfected with miR-19b inhibitor (unpaired t test, *P < 0.05). (E) MTT assay was used to measure the viability of H2O2-treated HaCaT cells that had been co-cultured with Exo-NC and Exo-inhibitor (unpaired t test, *P < 0.05). (F) Flow cytometry was implemented to measure the apoptosis of H2O2-treated HaCaT cells that had been co-cultured with Exo-NC and Exo-inhibitor (unpaired t test, *P < 0.05). (G) ELISA was utilized to measure the expression of apoptosis-related proteins (C-caspase3, Bcl-2) and inflammation-related proteins (IL-6, IL-10) in H2O2-treated HaCaT cells that had been co-cultured with Exo-NC and Exo-inhibitor (unpaired t test, *P < 0.05). (H) Wound healing was performed to measure the migration ability of H2O2-treated HaCaT cells that had been co-cultured with Exo-NC and Exo-inhibitor (unpaired t test, *P < 0.05).